Characterizing a CT esophagram protocol after flexible endoscopic diverticulotomy for Zenker's diverticulum: a retrospective series
- PMID: 36300156
- PMCID: PMC9469010
- DOI: 10.21037/tgh-20-269
Characterizing a CT esophagram protocol after flexible endoscopic diverticulotomy for Zenker's diverticulum: a retrospective series
Abstract
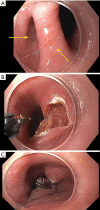
Background: Flexible endoscopic cricopharyngeal myotomy and septotomy offer a minimally invasive transluminal option for the treatment of symptomatic Zenker's diverticulum (ZD). There is currently no consensus regarding postoperative follow-up imaging. We suggest a standardized computed tomography (CT) esophagram protocol for radiographic evaluation of postoperative findings.
Methods: Single center retrospective analysis of patients with symptomatic ZD who underwent flexible endoscopic diverticulotomy and postoperative imaging with CT esophagram from January 2015 to March 2020. An experienced radiologist blinded to the initial imaging reports prospectively interpreted all CT esophagram findings, in order to minimize bias.
Results: Twenty-one patients underwent CT esophagram following flexible endoscopic diverticulotomy for ZD. Diverticulotomy was technically successful in all patients. Most common findings on imaging included: atelectasis (13/21; 62%), persistent esophageal diverticulum (7/21; 33%), pneumomediastinum (3/21; 14%), aspiration (2/21; 10%), and extraluminal air and contrast extravasation consistent with focal esophageal perforation (1/21; 5%).
Conclusions: We describe a standardized, simple, and accessible CT esophagram protocol for postoperative imaging of patients with post-flexible endoscopic cricopharyngeal myotomy and septotomy for ZD. CT esophagram facilitates a definitive exclusion of focal esophageal perforation as a postoperative complication of flexible endoscopic diverticulotomy by ruling out extraluminal air and contrast extravasation.
Keywords: Zenker’s diverticulum (ZD); diverticulotomy; endoscopy; esophagram; septotomy.
2022 Translational Gastroenterology and Hepatology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tgh.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tgh-20-269/coif). DY reports that he is a consultant for Boston Scientific, Lumendi, and Steris, outside the submitted work; PVD reports that he is a consultant for Boston Scientific, Olympus, Cook Medical, Lumendi, and Microtech, outside the submitted work. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
