Growth Differentiation Factor 15: A Novel Growth Biomarker for Children With Congenital Heart Disease
- PMID: 36300261
- PMCID: PMC10947752
- DOI: 10.1177/21501351221118080
Growth Differentiation Factor 15: A Novel Growth Biomarker for Children With Congenital Heart Disease
Abstract
Background: Failure to thrive (FTT), defined as weight or height less than the lowest 2.5 percentile for age, is prevalent in up to 66% of children with congenital heart disease (CHD). Risk stratification methods to identify those who would benefit from early intervention are currently lacking. We aimed to identify a novel growth biomarker to aid clinical decision-making in children with CHD.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study of patients 2 months to 10 years of age with any CHD undergoing cardiac surgery. Preoperative weight-for-age Z scores (WAZ) and height-for-age Z scores (HAZ) were calculated and assessed for association with preoperative plasma biomarkers: growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15), fibroblast growth factor 21, leptin, prealbumin, and C-reactive protein (CRP).
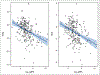
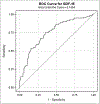
Results: Of the 238 patients included, approximately 70% of patients had WAZ/HAZ < 0 and 34% had FTT. There was a moderate correlation between GDF-15 and WAZ/HAZ. When stratified by age, the correlation of GDF-15 to WAZ and HAZ was strongest in children under 2 years of age and persisted in the setting of inflammation (CRP > 0.5 mg/dL). Diagnoses commonly associated with congestive heart failure had high proportions of FTT and median GDF-15 levels. Prealbumin was not correlated with WAZ or HAZ.
Conclusions: GDF-15 represents an important growth biomarker in children with CHD, especially those under 2 years of age who have diagnoses commonly associated with CHF. Our data do not support prealbumin as a long-term growth biomarker.
Keywords: cytokines; metabolism; nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

