Treatment of Post-Coarctectomy Hypertension With Labetalol-A 9-Year Single-Center Experience
- PMID: 36300272
- PMCID: PMC9615340
- DOI: 10.1177/21501351221111797
Treatment of Post-Coarctectomy Hypertension With Labetalol-A 9-Year Single-Center Experience
Abstract
Background: Although considering the pathophysiology of post-coarctectomy hypertension, β-blockers should be effective, experience with labetalol for treatment is limited in the literature.
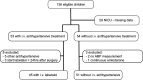
Methods: Retrospective collection and analysis of data in children aged ≤6 years following coarctectomy in our tertiary care university medical center between January 2009 and June 2018.
Results: 96 patients were included, 45 were treated with intravenous labetalol and 51 received no treatment. Median time to maximum dose received (median 1.1 mg/kg/h) was 2.7 h, and median time to the reduction of labetalol dose was 8.3 h. No antihypertensives had to be added. In one child, labetalol was switched to nitroprusside due to bronchoconstriction. Of patients receiving intravenous labetalol, 48% had been switched to oral labetalol at discharge.
Conclusions: Intravenous labetalol is a fast, effective, and safe drug to treat hypertension following aortic coarctation repair. Labetalol is easily converted to oral therapy when the continuation of treatment is considered necessary.
Keywords: aortic operation; coarctation; congenital heart surgery; database; intensive care; pediatric.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Tabbutt S, Nicolson SC, Adamson PC, et al. The safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of esmolol for blood pressure control immediately after repair of coarctation of the aorta in infants and children: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008;136(2):321-328. - PubMed
-
- Mery CM, Guzman-Pruneda FA, Trost JG, et al. Contemporary results of aortic coarctation repair through left thoracotomy. Ann Thorac Surg. 2015;100:1039-1046. - PubMed
-
- Moffet BS, Penny DJ. Variability in treatment of post-coarctectomy hypertension: a multicenter study. Pediatr Cardiol. 2016;37(4):772-777. - PubMed
-
- Charlton GA, Ladd DR, Friesen RM, Friesen RH. Labetalol infusion attenuates paradoxical hypertension and decreases plasma renin activity after repair of coarctation of the aorta in children. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2020;34(12):3348-3351. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

