Bilateral bi-level erector spinae plane blocks in scoliosis surgery: a retrospective comparative study
- PMID: 36300557
- PMCID: PMC9682554
- DOI: 10.5152/j.aott.2022.22019
Bilateral bi-level erector spinae plane blocks in scoliosis surgery: a retrospective comparative study
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to compare the effect of the ultrasound (US) guided erector spinae plane block (ESPB) on pain scores, opioid requirement, patient satisfaction, and the length of hospital stay with standard analgesia methods following scoliosis surgery.
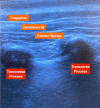
Methods: Twenty-seven patients (17 females, 10 males; mean age=15.59 ± 3.24 years) who underwent scoliosis surgery with preoperative bilateral bilevel US-guided ESPB were the sample group, and the remaining 30 patients (20 females, 10 males; mean age = 15.57 ± 2.75 years) without ESPB were the control group. Bilateral bilevel injection ESPB was performed at two levels (T4 and T10). Postoperative pain scores, morphine consumption, patient satisfaction scores, and the number of patients requiring rescue analgesia were recorded. A visual analog scale (VAS) was used to score postoperative pain.
Results: VAS at rest and when mobile, as well as postoperative cumulative morphine consumption in the first postoperative 24 h, was significantly lower in the ESPB group. Thirteen patients in the control group but no in the ESPB group required rescue analgesics in the postoperative period. Both the time to the requirement of the initial dose of PCA and patient satisfaction scores were significantly higher in the ESPB group (P < 0.001 for both).
Conclusion: Given the need for improved recovery of the patients, ESPB seems to be an essential analgesic technique that may reduce both opioid consumption and the severity of the pain, thus increasing the satisfaction of the patients and decreasing the length of hospital stay.
Level of evidence: Level IV, Therapeutic Study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bilateral Ultrasound-Guided Erector Spinae Plane Block for Perioperative Analgesia in Breast Reduction Surgery: A Prospective Randomized and Controlled Trial.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2023 Aug;47(4):1279-1288. doi: 10.1007/s00266-023-03315-0. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2023. PMID: 36928313 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of the effects of one-level and bi-level pre-incisional erector spinae plane block on postoperative acute pain in video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery; a prospective, randomized, double-blind trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 Aug 11;23(1):270. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02232-8. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 37568076 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Efficacy of Erector Spinae Plane Block Compared With Intrathecal Morphine in Postoperative Analgesia in Patients Undergoing Lumbar Spine Surgery: A Double-blind Prospective Comparative Study.Pain Physician. 2023 Mar;26(2):149-159. Pain Physician. 2023. PMID: 36988361 Clinical Trial.
-
Analgesic efficacy and safety of erector spinae plane block in breast cancer surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Anesthesiol. 2021 Feb 20;21(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12871-021-01277-x. BMC Anesthesiol. 2021. PMID: 33610172 Free PMC article.
-
Opioid-sparing multimodal analgesia with bilateral bi-level erector spinae plane blocks in scoliosis surgery: a case report of two patients.Eur Spine J. 2020 Dec;29(Suppl 2):138-144. doi: 10.1007/s00586-019-06133-8. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Eur Spine J. 2020. PMID: 31482311 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of the Bilateral and Bilevel Erector Spinae Plane Block (ESPB) in Pediatric Idiopathic Scoliosis Surgery: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Controlled Trial.J Pediatr Orthop. 2024 Aug 1;44(7):e634-e640. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000002707. Epub 2024 May 1. J Pediatr Orthop. 2024. PMID: 38689466 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Anesthetic Management of the Surgical Correction of Idiopathic Scoliosis in a Teenager With Ornithine Transcarbamalyse Deficiency.Cureus. 2023 Sep 17;15(9):e45393. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45393. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37854728 Free PMC article.
-
Erector spinae plane block in spine surgeries: Single-level versus bi-level, single-shot versus continuous catheter technique.Saudi J Anaesth. 2024 Jan-Mar;18(1):105-107. doi: 10.4103/sja.sja_775_23. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Saudi J Anaesth. 2024. PMID: 38313725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety and efficacy of erector spinae plane block for perioperative analgesia in posterior spinal fusion surgery for pediatric idiopathic scoliosis: a meta-analysis.Spine Deform. 2025 Jul 15. doi: 10.1007/s43390-025-01145-5. Online ahead of print. Spine Deform. 2025. PMID: 40665030 Review.
-
Multi-level bilateral ultrasound-guided retrolaminar block for fast-track spinal deformity surgery.Saudi J Anaesth. 2024 Jul-Sep;18(3):464-466. doi: 10.4103/sja.sja_122_24. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Saudi J Anaesth. 2024. PMID: 39149741 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials