Stafiba: A STAT5-Selective Small-Molecule Inhibitor
- PMID: 36300584
- PMCID: PMC10099813
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.202200553
Stafiba: A STAT5-Selective Small-Molecule Inhibitor
Abstract
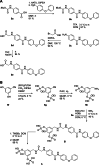
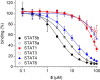
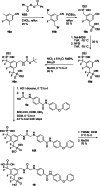
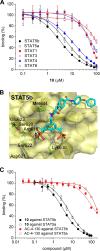
The transcription factors STAT5a and STAT5b are constitutively active in many human tumors. Combined inhibition of both STAT5 proteins is a valuable approach with promising applications in tumor biology. We recently reported resorcinol bisphosphate as a moderately active inhibitor of the protein-protein interaction domains, the SH2 domains, of both STAT5a and STAT5b. Here, we describe the development of resorcinol bisphosphate to Stafiba, a phosphatase-stable inhibitor of STAT5a and STAT5b with activity in the low micromolar concentration range. Our data provide insights into the structure-activity relationships of resorcinol bisphosphates and the corresponding bisphosphonates for use as inhibitors of both STAT5a and STAT5b.
Keywords: SH2 domains; biological activity; inhibitors; protein-protein interactions; transcription factors.
© 2022 The Authors. ChemBioChem published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
T.B. is an inventor on the German patent DE102015201148.8 B4 covering the potential use of phenyl phosphates and their prodrugs as drugs for cancer therapy.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

