FtsK, a DNA Motor Protein, Coordinates the Genome Segregation and Early Cell Division Processes in Deinococcus radiodurans
- PMID: 36300930
- PMCID: PMC9764985
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.01742-22
FtsK, a DNA Motor Protein, Coordinates the Genome Segregation and Early Cell Division Processes in Deinococcus radiodurans
Abstract
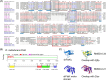
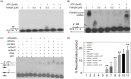
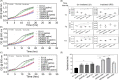
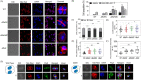
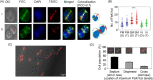
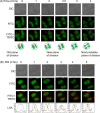
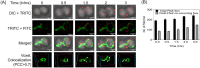
Filament temperature-sensitive mutant K (FtsK)/SpoIIIE family proteins are DNA translocases known as the fastest DNA motor proteins that use ATP for their movement on DNA. Most of the studies in single chromosome-containing bacteria have established the role of FtsK in chromosome dimer resolution (CDR), connecting the bacterial chromosome segregation process with cell division. Only limited reports, however, are available on the interdependent regulation of genome segregation and cell division in multipartite genome harboring (MGH) bacteria. In this study, for the first time, we report the characterization of FtsK from the radioresistant MGH bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans R1 (drFtsK). drFtsK shows the activity characteristics of a typical FtsK/SpoIIIE/Tra family. It stimulates the site-specific recombination catalyzed by Escherichia coli tyrosine recombinases. drFtsK interacts with various cell division and genome segregation proteins of D. radiodurans. Microscopic examination of different domain deletion mutants of this protein reveals alterations in cellular membrane architecture and nucleoid morphology. In vivo localization studies of drFtsK-RFP show that it forms multiple foci on nucleoid as well as on the membrane with maximum density on the septum. drFtsK coordinates its movement with nucleoid separation. The alignment of its foci shifts from old to new septum indicating its cellular dynamics with the FtsZ ring during the cell division process. Nearly, similar positional dynamicity of FtsK was observed in cells recovering from gamma radiation exposure. These results suggest that FtsK forms a part of chromosome segregation, cell envelope, and cell division machinery in D. radiodurans. IMPORTANCE Deinococcus radiodurans show extraordinary resistance to gamma radiation. It is polyploid and harbors a multipartite genome comprised of 2 chromosomes and 2 plasmids, packaged in a doughnut-shaped toroidal nucleoid. Very little is known about how the tightly packed genome is accurately segregated and the next divisional plane is determined. Filament temperature-sensitive mutant K (FtsK), a multifunctional protein, helps in pumping the septum-trapped DNA in several bacteria. Here, we characterized FtsK of D. radiodurans R1 (drFtsK) for the first time and showed it to be an active protein. The absence of drFtsK causes many defects in morphology at both cellular and nucleoid levels. The compact packaging of the deinococcal genome and cell membrane formation is hindered in ftsK mutants. In vivo drFtsK is dynamic, forms foci on both nucleoid and septum, and coordinates with FtsZ for the next cell division. Thus, drFtsK role in maintaining the normal genome phenotype and cell division in D. radiodurans is suggested.
Keywords: DNA translocation; Deinococcus radiodurans; FtsK; bacterial cell division.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
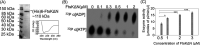

Similar articles
-
DivIVA Regulates Its Expression and the Orientation of New Septum Growth in Deinococcus radiodurans.J Bacteriol. 2021 Jul 8;203(15):e0016321. doi: 10.1128/JB.00163-21. Epub 2021 Jul 8. J Bacteriol. 2021. PMID: 34031039 Free PMC article.
-
Topoisomerase IB interacts with genome segregation proteins and is involved in multipartite genome maintenance in Deinococcus radiodurans.Microbiol Res. 2021 Jan;242:126609. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2020.126609. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Microbiol Res. 2021. PMID: 33059113
-
ParA encoded on chromosome II of Deinococcus radiodurans binds to nucleoid and inhibits cell division in Escherichia coli.J Biosci. 2013 Sep;38(3):487-97. doi: 10.1007/s12038-013-9352-5. J Biosci. 2013. PMID: 23938382
-
FtsK and SpoIIIE, coordinators of chromosome segregation and envelope remodeling in bacteria.Trends Microbiol. 2022 May;30(5):480-494. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2021.10.002. Epub 2021 Oct 30. Trends Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34728126 Review.
-
FtsK, a literate chromosome segregation machine.Mol Microbiol. 2007 Jun;64(6):1434-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05755.x. Epub 2007 May 18. Mol Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17511809 Review.
Cited by
-
A new paradigm for the regulation of A40926B0 biosynthesis.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2025 Apr 7;10(3):794-806. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2025.03.012. eCollection 2025 Sep. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40297762 Free PMC article.
-
Differential cellular localization of DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IB in response to DNA damage in Deinococcus radiodurans.Extremophiles. 2023 Dec 7;28(1):7. doi: 10.1007/s00792-023-01323-1. Extremophiles. 2023. PMID: 38062175
-
Leptospira interrogans biofilm transcriptome highlights adaption to starvation and general stress while maintaining virulence.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024 Sep 30;10(1):95. doi: 10.1038/s41522-024-00570-0. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024. PMID: 39349472 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics of Deinococcus radiodurans: unveiling genetic discrepancies between ATCC 13939K and BAA-816 strains.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jun 19;15:1410024. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1410024. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38962131 Free PMC article.
-
Complete genome sequence of Deinococcus rubellus Ant6 isolated from the fish muscle in the Antarctic Ocean.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Oct 16;11:1257705. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1257705. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37908375 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

