SETD6 Regulates E2-Dependent Human Papillomavirus Transcription
- PMID: 36300937
- PMCID: PMC9682981
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01295-22
SETD6 Regulates E2-Dependent Human Papillomavirus Transcription
Abstract
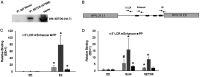
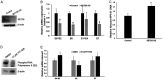
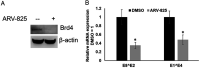
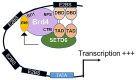
Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (Brd4) is a member of the bromodomain and extraterminal domain (BET) family of proteins. Brd4 regulates human papillomavirus (HPV) transcription, genome replication, and segregation by binding to the E2 protein. The SETD6 methyltransferase binds to and methylates Brd4 at lysine 99. We investigated the interactions of SETD6 and Brd4 with E2 and their role in HPV transcription. SETD6 coimmunoprecipitated with the E2 transactivation domain, and its depletion in CIN612 episomal cells reduced human papillomavirus type 31 (HPV-31) transcription, whereas depletion of SETD6 in integrated HPV cell lines had no effect on viral gene expression. The mutant Brd4 K99R (bearing a change of K to R at position 99), which cannot be methylated by SETD6, displayed decreased binding to HPV-31 E2, suggesting that SETD6 methylation of Brd4 also influences E2 association with the Brd4 protein. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation, SETD6 was detected at the enhancer region of the HPV long control region. We propose that methylation of Brd4 at K99 by SETD6 is an important mechanism for E2-Brd4 association and HPV transcriptional activation. IMPORTANCE Human papillomaviruses (HPV) cause cervical, anogenital, and oral cancers. Brd4 plays an important role in the HPV life cycle. SETD6 was recently shown to methylate Brd4. The current study demonstrates that methylation of Brd4 by SETD6 in HPV-episomal cells is required for the activation of viral transcription. This study illustrates a novel regulatory mechanism involving E2, Brd4, and SETD6 in the HPV life cycle and provides insight into the multiple roles of Brd4 in viral pathogenesis.
Keywords: Brd4; HPV; SETD6; transcriptional regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

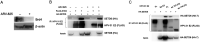

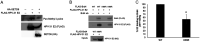

Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation of a Conserved Tyrosine in the Papillomavirus E2 Protein Regulates Brd4 Binding and Viral Replication.J Virol. 2019 May 1;93(10):e01801-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01801-18. Print 2019 May 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30842331 Free PMC article.
-
The cellular bromodomain protein Brd4 has multiple functions in E2-mediated papillomavirus transcription activation.Viruses. 2014 Aug 20;6(8):3228-49. doi: 10.3390/v6083228. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 25140737 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of Brd4 to the human papillomavirus type 16 DNA replication complex is essential for replication of viral DNA.J Virol. 2013 Apr;87(7):3871-84. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03068-12. Epub 2013 Jan 30. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23365439 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Brd4 in different steps of the papillomavirus life cycle.Virus Res. 2017 Mar 2;231:76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.12.006. Epub 2016 Dec 10. Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 27965149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The double bromodomain-containing chromatin adaptor Brd4 and transcriptional regulation.J Biol Chem. 2007 May 4;282(18):13141-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R700001200. Epub 2007 Feb 28. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17329240 Review.
Cited by
-
Senataxin mediates R-loop resolution on HPV episomes.J Virol. 2024 Aug 20;98(8):e0100324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01003-24. Epub 2024 Jul 24. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39046232 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of R-Loops in DNA Tumor Viruses.Pathogens. 2024 Oct 2;13(10):863. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13100863. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39452734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orchestrating epigenetics: a comprehensive review of the methyltransferase SETD6.Exp Mol Med. 2025 Mar;57(3):533-544. doi: 10.1038/s12276-025-01423-2. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Exp Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40102573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focal Adhesion Kinase Binds to the HPV E2 Protein to Regulate Initial Replication after Infection.Pathogens. 2023 Sep 28;12(10):1203. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12101203. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37887719 Free PMC article.
-
Development of human papillomavirus and its detection methods (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2024 Jul 31;28(4):382. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12671. eCollection 2024 Oct. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 39161614 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

