MicroRNA-582-5p targeting Creb1 modulates apoptosis in cardiomyocytes hypoxia/reperfusion-induced injury
- PMID: 36301033
- PMCID: PMC9601879
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.708
MicroRNA-582-5p targeting Creb1 modulates apoptosis in cardiomyocytes hypoxia/reperfusion-induced injury
Abstract
Background: Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (MIRI) caused by the reperfusion therapy of myocardial ischemic diseases is a kind of major disease that threatens human health and lives severely. There are lacking of effective therapeutic measures for MIRI. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are abundant in mammalian species and play a critical role in the initiation, promotion, and progression of MIRI. However, the biological role and molecular mechanism of miRNAs in MIRI are not entirely clear.
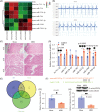
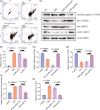
Methods: We used bioinformatics analysis to uncover the significantly different miRNA by analyzing transcriptome sequencing data from myocardial tissue in the mouse MIRI model. Multiple miRNA-related databases, including miRdb, PicTar, and TargetScan were used to forecast the downstream target genes of the differentially expressed miRNA. Then, the experimental models, including male C57BL/6J mice and HL-1 cell line, were used for subsequent experiments including quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis, western blot analysis, hematoxylin and eosin staining, flow cytometry, luciferase assay, gene interference, and overexpression.
Results: MiR-582-5p was found to be differentially upregulated from the transcriptome sequencing data. The elevated levels of miR-582-5p were verified in MIRI mice and hypoxia/reperfusion (H/R)-induced HL-1 cells. Functional experiments revealed that miR-582-5p promoted apoptosis of H/R-induced HL-1 cells via downregulating cAMP-response element-binding protein 1 (Creb1). The inhibiting action of miR-582-5p inhibitor on H/R-induced apoptosis was partially reversed after Creb1 interference.
Conclusions: Collectively, the research findings reported that upregulation of miR-582-5p promoted H/R-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by inhibiting Creb1. The potential diagnostic and therapeutic strategies targeting miR-582-5p and Creb1 could be beneficial for the MIRI treatment.
Keywords: Creb1; apoptosis; miR-582-5p; myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
© 2022 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Griffiths K, Lee JJ, Frenneaux MP, Feelisch M, Madhani M. Nitrite and myocardial ischaemia reperfusion injury. Where are we now? Pharmacol Ther. 2021;223:107819. - PubMed
-
- Xiong W, Qu Y, Chen H, Qian J. Insight into long noncoding RNA‐miRNA‐mRNA axes in myocardial ischemia‐reperfusion injury: the implications for mechanism and therapy. Epigenomics. 2019;11(15):1733‐1748. - PubMed
-
- Heusch G. Myocardial ischaemia‐reperfusion injury and cardioprotection in perspective. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17(12):773‐789. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

