Emergence of an Extensive Drug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strain of Chicken Origin Carrying blaIMP-45, tet(X6), and tmexCD3- toprJ3 on an IncpRBL16 Plasmid
- PMID: 36301093
- PMCID: PMC9769874
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.02283-22
Emergence of an Extensive Drug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strain of Chicken Origin Carrying blaIMP-45, tet(X6), and tmexCD3- toprJ3 on an IncpRBL16 Plasmid
Abstract
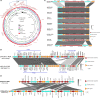
This study reports an extensively drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PA166-2 which was of chicken origin and carrying blaIMP-45, tet(X6) and tmexCD3-toprJ3 on a single plasmid. The strain was characterized by antimicrobial susceptibility testing, resistance gene screening, conjugation assay, whole-genome sequencing, and bioinformatics analysis. Strain PA166-2 was resistant to tigecycline and carbapenems. It belonged to ST313 and carried a plasmid pPA166-2-MDR, which belongs to the incompatibility group IncpRBL16. pPA166-2-MDR harbored a 78 Kb multidrug resistance (MDR) region carrying an array of antimicrobial resistance genes, including blaIMP-45, tet(X6), and tmexCD3-toprJ3. The gene blaIMP-45 was inserted into the backbone of plasmid pPA166-2-MDR within a class 1 integron, In786. tmexCD3-toprJ3 in plasmid pPA166-2-MDR was inserted in umuC, constituting the genetic context of ISCfr1-tnfxB3-tmexC3-tmexD3-toprJ3-△umuC. The genetic context of tet(X6) in this plasmid was identical to that of other reported plasmid-borne tet(X) variants, namely, tet(X6)-abh-guaA-ISVsa3. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of the cooccurrence of blaIMP-45, tet(X6), and tmexCD3-toprJ3 in one plasmid in Pseudomonas sp. The emergence of plasmid-mediated tigecycline resistance genes tmexCD3-toprJ3 and tet(X6), as well as carbapenemase genes from chickens expanded the global transmission of vital resistance genes. Findings from us and from others indicate that plasmids of the incompatibility group IncpRBL16 may serve as a reservoir for carbapenem and tigecycline resistance determinants. IMPORTANCE Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic pathogen that causes infections that are difficult to treat. This study reported, for the first time, the occurrence of last-resort antibiotic resistance determinants blaIMP-45, tet(X6), and tmexCD3-toprJ3 on a single plasmid in P. aeruginosa from chickens. The P. aeruginosa strain belonged to ST313 and was resistant to last-line antibiotics, namely, carbapenems and tigecycline. The plasmid carrying the last-line resistance genes belonged to the incompatibility group IncpRBL16, which was reported to contain different profiles of accessory modules and thus carried diverse collections of resistance genes. The emergence of plasmid-mediated tigecycline resistance genes tmexCD3-toprJ3 and tet(X6), as well as carbapenemase genes, from chickens expanded the global transmission of vital resistance genes. The results in this study highlighted that IncpRBL16 plasmids may serve as a reservoir for the dissemination of resistance genes. Control measures should be implemented to prevent the further dissemination of such strains.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; blaIMP-45; extensive drug resistance; tet(X6); tmexCD3-toprJ3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Transferable IncC-IncX3 Hybrid Plasmid Cocarrying blaNDM-4, tet(X), and tmexCD3-toprJ3 Confers Resistance to Carbapenem and Tigecycline.mSphere. 2021 Aug 25;6(4):e0059221. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00592-21. Epub 2021 Aug 4. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34346701 Free PMC article.
-
Novel tigecycline resistance gene cluster tnfxB3-tmexCD3-toprJ1b in Proteus spp. and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, co-existing with tet(X6) on an SXT/R391 integrative and conjugative element.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021 Nov 12;76(12):3159-3167. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkab325. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021. PMID: 34508611
-
Emergence of the resistance-nodulation-division efflux pump tmexCD3-toprJ3 gene confers resistance to tigecycline in Pseudomonas juntendi and Proteus terrae isolated from a pig farm in China.Vet Med Sci. 2022 Nov;8(6):2460-2465. doi: 10.1002/vms3.950. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Vet Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 36130135 Free PMC article.
-
Dissemination and prevalence of plasmid-mediated high-level tigecycline resistance gene tet (X4).Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 29;13:969769. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.969769. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36246244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of tigecycline-resistance among Enterobacterales.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Apr 9;14:1289396. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1289396. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38655285 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tracing the evolutionary trajectory of the IncP-2 plasmid co-harboring bla IMP-45 and bla VIM-1: an outbreak of Pseudomonas aeruginosa co-producing IMP-45 and VIM-1 carbapenemases in China.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jun 19;15:1623241. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1623241. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40612392 Free PMC article.
-
Prioritization of Critical Factors for Surveillance of the Dissemination of Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 15;24(20):15209. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015209. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894890 Free PMC article.
-
Global phylogeography and genetic characterization of carbapenem and ceftazidime-avibactam resistant KPC-33-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa.NPJ Antimicrob Resist. 2025 Jan 7;3(1):3. doi: 10.1038/s44259-024-00073-0. NPJ Antimicrob Resist. 2025. PMID: 39843962 Free PMC article.
-
Binding assays enable discovery of Tet(X) inhibitors that combat tetracycline destructase resistance.Chem Sci. 2025 May 7;16(22):9691-9704. doi: 10.1039/d5sc00964b. eCollection 2025 Jun 4. Chem Sci. 2025. PMID: 40342919 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of quorum sensing and biofilm formation on antimicrobial resistance and virulence of XDR and MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa in laying chickens.Iran J Vet Res. 2024;25(2):125-134. doi: 10.22099/IJVR.2024.47975.6969. Iran J Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39624194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lv L, Wan M, Wang C, Gao X, Yang Q, Partridge SR, Wang Y, Zong Z, Doi Y, Shen J, Jia P, Song Q, Zhang Q, Yang J, Huang X, Wang M, Liu J-H. 2020. Emergence of a plasmid-encoded resistance-nodulation-division efflux pump conferring resistance to multiple drugs, including tigecycline, in Klebsiella pneumoniae. mBio 11:e02930-19. doi:10.1128/mBio.02930-19. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sun S, Gao H, Liu Y, Jin L, Wang R, Wang X, Wang Q, Yin Y, Zhang Y, Wang H. 2020. Co-existence of a novel plasmid-mediated efflux pump with colistin resistance gene mcr in one plasmid confers transferable multidrug resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Emerg Microbes Infect 9:1102–1113. doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1768805. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

