Torquetenovirus viral load is associated with anti-spike antibody response in SARS-CoV-2 mRNA BNT162b2 vaccinated kidney transplant patients
- PMID: 36301197
- PMCID: PMC9874652
- DOI: 10.1111/ctr.14825
Torquetenovirus viral load is associated with anti-spike antibody response in SARS-CoV-2 mRNA BNT162b2 vaccinated kidney transplant patients
Abstract
Introduction: Kidney transplant patients (KT) are at high risk for severe COVID-19 and presented attenuated antibody responses to vaccination when compared to immunocompetent individuals. Torquetenovirus (TTV) has recently gained attention as a potential surrogate marker of the net state of immunosuppression. We evaluated the association between pre-vaccination TTV viral load and anti-spike total antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in KT.
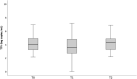
Material and methods: The 114 adult KT recipients enrolled in this prospective single-center cohort study received two doses of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine. Serum samples were collected immediately before vaccination at the days when patients received both the first (T0) and the second dose (T1) and 16-45 days after the second dose (T2). Primary endpoint was the development of anti-spike total antibodies after vaccination. Demographic, clinical, and laboratorial parameters were compared between patients with and without detectable SARS-CoV-2 antibodies at T2.
Results: Ninety-nine patients (86.8%) were naïve for SARS-CoV-2 before vaccination. Fifty-six (56.6%) patients developed anti-spike total antibodies at T2. The use of mTOR inhibitors was associated with a favorable response (p = .005); conversely, mycophenolic acid (MPA) was associated with a negative response (p = .006). In a multivariable model, the presence of TTV at T0 ≥ 3.36 log10 cp/ml was associated with unfavorable vaccine response (OR: 5.40; 95% CI: 1.47-19.80; p = .011), after adjusting for age and eGFR at T0.
Conclusions: Higher TTV viral loads before vaccination are associated with reduced anti-spike total antibody response in SARS-CoV-2 mRNA BNT162b2 vaccinated KT patients. The association between TTV viral load and vaccine response may be an added-value in the optimization of vaccination regimens in KT.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; kidney transplantation; torquetenovirus; vaccine.
© 2022 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous