GluA2-lacking AMPA receptors in the nucleus accumbens core and shell contribute to the incubation of oxycodone craving in male rats
- PMID: 36301206
- PMCID: PMC10655598
- DOI: 10.1111/adb.13237
GluA2-lacking AMPA receptors in the nucleus accumbens core and shell contribute to the incubation of oxycodone craving in male rats
Abstract
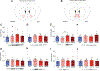
One of the most challenging issues in the treatment of substance use disorder, including misuse of opioids such as oxycodone, is persistent vulnerability to relapse, often triggered by cues or contexts previously associated with drug use. In rats, cue-induced craving progressively intensifies ('incubates') during withdrawal from extended-access self-administration of several classes of misused drugs, including the psychostimulants cocaine and methamphetamine. For these psychostimulants, incubation is associated with strengthening of excitatory synapses in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) through incorporation of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid receptors that lack the GluA2 subunit and are therefore Ca2+ -permeable (CP-AMPARs). Once CP-AMPAR upregulation occurs, their stimulation is required for expression of incubation. It is not known if a similar mechanism contributes to incubation of oxycodone craving. Using male rats, we established that incubation occurs by withdrawal day (WD) 15 and persists through WD30. Then, using cell-surface biotinylation, we found that surface levels of the AMPAR subunit GluA1 but not GluA2 are elevated in NAc core and shell of oxycodone rats on WD15, although this wanes by WD30. Next, using intra-NAc injection of the selective CP-AMPAR antagonist Naspm before a seeking test, we demonstrate that CP-AMPAR blockade in either subregion decreases oxycodone seeking on WD15 or WD30 (after incubation), but not WD1, and has no effect in saline self-administering animals. The Naspm results suggest CP-AMPARs persist in synapses through WD30 even if total cell surface levels wane. These results suggest that a common neurobiological mechanism contributes to expression of incubation of craving for oxycodone and psychostimulants.
Keywords: incubation of craving; nucleus accumbens; oxycodone.
© 2022 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no competing interests and have nothing to disclose.
Figures
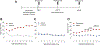
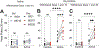
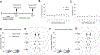

Similar articles
-
AMPA Receptor Plasticity in Accumbens Core Contributes to Incubation of Methamphetamine Craving.Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Nov 1;80(9):661-670. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.04.003. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27264310 Free PMC article.
-
AMPA receptor and metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 adaptations in the nucleus accumbens core during incubation of methamphetamine craving.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019 Aug;44(9):1534-1541. doi: 10.1038/s41386-019-0425-5. Epub 2019 May 30. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019. PMID: 31146278 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-permeable AMPA receptors are present in nucleus accumbens synapses after prolonged withdrawal from cocaine self-administration but not experimenter-administered cocaine.J Neurosci. 2011 Apr 13;31(15):5737-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0350-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21490215 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptations in AMPA receptor transmission in the nucleus accumbens contributing to incubation of cocaine craving.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt B(0 0):287-300. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.061. Epub 2013 May 30. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23727437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of AMPA receptor trafficking in the nucleus accumbens by dopamine and cocaine.Neurotox Res. 2010 Nov;18(3-4):393-409. doi: 10.1007/s12640-010-9176-0. Epub 2010 Apr 2. Neurotox Res. 2010. PMID: 20361291 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1A (ASIC1A) in the Behavioral and Synaptic Effects of Oxycodone and Other Opioids.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 29;25(21):11584. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111584. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519136 Free PMC article.
-
Orbitofrontal cortex to dorsal striatum circuit is critical for incubation of oxycodone craving after forced abstinence.Addict Biol. 2024 Oct;29(10):e13440. doi: 10.1111/adb.13440. Addict Biol. 2024. PMID: 39380299 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiology of the incubation of drug craving: An update.Pharmacol Rev. 2025 Mar;77(2):100022. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmr.2024.100022. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Pharmacol Rev. 2025. PMID: 40148031 Review.
-
Sex-specific behavioral and thalamo-accumbal circuit adaptations after oxycodone abstinence.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 7:2024.08.01.605459. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.01.605459. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39149276 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor function and regulation of sleep-wake cycles.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2023;168:93-175. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2022.11.002. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36868636 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

