Embryonic ethanol exposure induces ectopic Hcrt and MCH neurons outside hypothalamus in rats and zebrafish: Role in ethanol-induced behavioural disturbances
- PMID: 36301208
- PMCID: PMC9625080
- DOI: 10.1111/adb.13238
Embryonic ethanol exposure induces ectopic Hcrt and MCH neurons outside hypothalamus in rats and zebrafish: Role in ethanol-induced behavioural disturbances
Abstract
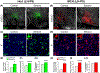
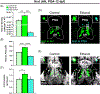
Embryonic exposure to ethanol increases the risk for alcohol use disorder in humans and stimulates alcohol-related behaviours in different animal models. Evidence in rats and zebrafish suggests that this phenomenon induced by ethanol at low-moderate concentrations involves a stimulatory effect on neurogenesis and density of hypothalamic neurons expressing the peptides, hypocretin/orexin (Hcrt) and melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH), known to promote alcohol consumption. Building on our report in zebrafish showing that ethanol induces ectopic expression of Hcrt neurons outside the hypothalamus, we investigated here whether embryonic ethanol exposure also induces ectopic peptide neurons in rats similar to zebrafish and affects their morphological characteristics and if these ectopic neurons are functional and have a role in the ethanol-induced disturbances in behaviour. We demonstrate in rats that ethanol at a low-moderate dose, in addition to increasing Hcrt and MCH neurons in the lateral hypothalamus where they are normally concentrated, induces ectopic expression of these peptide neurons further anterior in the nucleus accumbens core and ventromedial caudate putamen where they have not been previously observed and causes morphological changes relative to normally located hypothalamic neurons. Similar to rats, embryonic ethanol exposure at a low-moderate dose in zebrafish induces ectopic Hcrt neurons anterior to the hypothalamus and alters their morphology. Notably, laser ablation of these ectopic Hcrt neurons blocks the behavioural effects induced by ethanol exposure, including increased anxiety and locomotor activity. These findings suggest that the ectopic peptide neurons are functional and contribute to the ethanol-induced behavioural disturbances related to the overconsumption of alcohol.
Keywords: alcohol; ectopic neurons; embryonic ethanol.
© 2022 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Moderate Prenatal Ethanol Exposure Stimulates CXCL12/CXCR4 Chemokine System in Radial Glia Progenitor Cells in Hypothalamic Neuroepithelium and Peptide Neurons in Lateral Hypothalamus of the Embryo and Postnatal Offspring.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020 Apr;44(4):866-879. doi: 10.1111/acer.14296. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020. PMID: 32020622 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Chemokine Cxcl12a in Mediating the Stimulatory Effects of Ethanol on Embryonic Development of Subpopulations of Hypocretin/Orexin Neurons and Their Projections.Cells. 2023 May 16;12(10):1399. doi: 10.3390/cells12101399. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37408233 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal ethanol consumption before paternal fertilization: Stimulation of hypocretin neurogenesis and ethanol intake in zebrafish offspring.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Jan 10;96:109728. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109728. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 31394141 Free PMC article.
-
The Hypocretin/Orexin Neuronal Networks in Zebrafish.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2017;33:75-92. doi: 10.1007/7854_2016_59. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28012092 Review.
-
Pleasure, addiction, and hypocretin (orexin).Handb Clin Neurol. 2021;180:359-374. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-820107-7.00022-7. Handb Clin Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34225941 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding zebrafish sleep and wakefulness physiology as an experimental model for biomedical research.Fish Physiol Biochem. 2024 Apr;50(2):827-842. doi: 10.1007/s10695-023-01288-0. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38150068 Review.
-
Sleep Loss and Substance Use Disorders: An Issue from Adolescents to Adults.Behav Sci (Basel). 2025 Feb 15;15(2):220. doi: 10.3390/bs15020220. Behav Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40001851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utility of the Zebrafish Model for Studying Neuronal and Behavioral Disturbances Induced by Embryonic Exposure to Alcohol, Nicotine, and Cannabis.Cells. 2023 Oct 23;12(20):2505. doi: 10.3390/cells12202505. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37887349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of hypothalamic orexin (hypocretin) circuits to pathologies of motivation.Br J Pharmacol. 2024 Nov;181(22):4430-4449. doi: 10.1111/bph.17325. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Br J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39317446 Review.
-
Melanin-Concentrating Hormone (MCH): Role in Mediating Reward-Motivated and Emotional Behavior and the Behavioral Disturbances Produced by Repeated Exposure to Reward Substances.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 24;26(15):7143. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157143. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806293 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gupta KK, Gupta VK, Shirasaka T. An Update on Fetal Alcohol Syndrome-Pathogenesis, Risks, and Treatment. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016;40(8):1594–1602. - PubMed
-
- Skofitsch G, Jacobowitz DM, Zamir N. Immunohistochemical localization of a melanin concentrating hormone-like peptide in the rat brain. Brain Res Bull. 1985;15(6):635–649. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

