Nucleoplasmic lamin C rapidly accumulates at sites of nuclear envelope rupture with BAF and cGAS
- PMID: 36301259
- PMCID: PMC9617480
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202201024
Nucleoplasmic lamin C rapidly accumulates at sites of nuclear envelope rupture with BAF and cGAS
Abstract
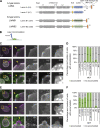
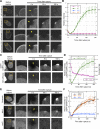
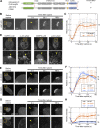
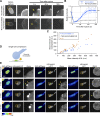
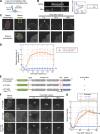
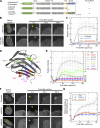
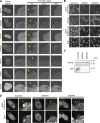
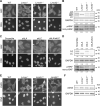
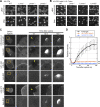
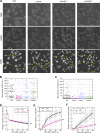
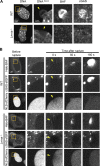
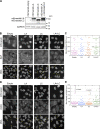
In mammalian cell nuclei, the nuclear lamina (NL) underlies the nuclear envelope (NE) to maintain nuclear structure. The nuclear lamins, the major structural components of the NL, are involved in the protection against NE rupture induced by mechanical stress. However, the specific role of the lamins in repair of NE ruptures has not been fully determined. Our analyses using immunofluorescence and live-cell imaging revealed that the nucleoplasmic pool of lamin C rapidly accumulated at sites of NE rupture induced by laser microirradiation in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. The accumulation of lamin C at the rupture sites required both the immunoglobulin-like fold domain that binds to barrier-to-autointegration factor (BAF) and a nuclear localization signal. The accumulation of nuclear BAF and cytoplasmic cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) at the rupture sites was in part dependent on lamin A/C. These results suggest that nucleoplasmic lamin C, BAF, and cGAS concertedly accumulate at sites of NE rupture for rapid repair.
© 2022 Kono et al.
Figures




References
-
- Akinci, B., Onay H., Demir T., Savas-Erdeve S., Gen R., Simsir I.Y., Keskin F.E., Erturk M.S., Uzum A.K., Yaylali G.F., et al. 2017. Clinical presentations, metabolic abnormalities and end-organ complications in patients with familial partial lipodystrophy. Metabolism. 72:109–119. 10.1016/j.metabol.2017.04.010 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Béréziat, V., Cervera P., Le Dour C., Verpont M.C., Dumont S., Vantyghem M.C., Capeau J., Vigouroux C., and Lipodystrophy Study G.. 2011. LMNA mutations induce a non-inflammatory fibrosis and a brown fat-like dystrophy of enlarged cervical adipose tissue. Am. J. Pathol. 179:2443–2453. 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.07.049 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biamonti, G., Giacca M., Perini G., Contreas G., Zentilin L., Weighardt F., Guerra M., Della Valle G., Saccone S., Riva S., and Falaschi A.. 1992. The gene for a novel human lamin maps at a highly transcribed locus of chromosome 19 which replicates at the onset of S-phase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 12:3499–3506. 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3499-3506.1992 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bonne, G., Di Barletta M.R., Varnous S., Bécane H.M., Hammouda E.H., Merlini L., Muntoni F., Greenberg C.R., Gary F., Urtizberea J.A., et al. 1999. Mutations in the gene encoding lamin A/C cause autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Nat. Genet. 21:285–288. 10.1038/6799 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

