Low serum uromodulin levels and their association with lupus flares
- PMID: 36301848
- PMCID: PMC9612514
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276481
Low serum uromodulin levels and their association with lupus flares
Abstract
Background: Only two previous studies in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients have identified that the blood concentrations of uromodulin are lower in nephritis. However, none of them had evaluated whether a low serum uromodulin adjusted by the glomerular filtration rate (sUromod/eGFR index) contributed to identify patients in risk of lupus nephritis (LN) using multivariable models.
Aim: Therefore, this study aimed two objectives to evaluate the association between low serum uromodulin levels and low sUromod adjusted by eGFR with renal flares in SLE excluding effects of potential confounders in multivariable analyses; and to identify the value of low sUmod and low sUmod/eGFR index as a potential diagnostic marker of LN.
Patients and methods: Design: Cross-sectional study. SLE patients (n = 114) were investigated for lupus flare with renal SLEDAI. Two groups: a) SLE with renal flare (renal-SLEDAI≥4, n = 41) and b) SLE non-renal flare (renal SLEDAI<4, n = 73). SLE patients were evaluated by other indices including a global disease activity index (SLEDAI) and SLICC renal disease activity score. Serum uromodulin levels (ng/mL) were quantified by ELISA. Serum uromodulin was adjusted by eGFR (sUromod/eGFR index). Cutt-offs of low sUromodulin and low sUromod/eGFR index were computed, ROC curves were performed and values of diagnostic tests were obtained. Multivariable logistic regression models were performed to identify if low sUromod/eGFR index is associated to renal flares.
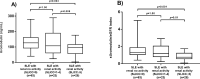
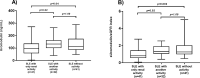
Results: Low serum uromodulin and low sUromod/eGFR index correlated to high scores of renal-SLEDAI, SLICC-renal and proteinuria. SLE patients with a renal flare had lower uromodulin levels compared to SLE patients without renal flare (p = 0.004). After adjusting by potential confounders, the low sUromod/eGFR index (<0.80 ng/mL) increased the risk of a renal flare (OR, 2.91; 95%CI, 1.21 to 6.98; p = 0.02).
Conclusions: We propose the low sUromod/eGFR index as a potential new marker of renal disease activity in SLE.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Kostopoulou M, Fanouriakis A, Cheema K, Boletis J, Bertsias G, Jayne D, et al.. Management of lupus nephritis: A systematic literature review informing the 2019 update of the joint EULAR and European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association (EULAR/ERA-EDTA) recommendations. RMD Open. 2020;6. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001263 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

