A CNN-transformer fusion network for COVID-19 CXR image classification
- PMID: 36301907
- PMCID: PMC9612494
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276758
A CNN-transformer fusion network for COVID-19 CXR image classification
Abstract
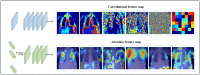
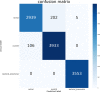
The global health crisis due to the fast spread of coronavirus disease (Covid-19) has caused great danger to all aspects of healthcare, economy, and other aspects. The highly infectious and insidious nature of the new coronavirus greatly increases the difficulty of outbreak prevention and control. The early and rapid detection of Covid-19 is an effective way to reduce the spread of Covid-19. However, detecting Covid-19 accurately and quickly in large populations remains to be a major challenge worldwide. In this study, A CNN-transformer fusion framework is proposed for the automatic classification of pneumonia on chest X-ray. This framework includes two parts: data processing and image classification. The data processing stage is to eliminate the differences between data from different medical institutions so that they have the same storage format; in the image classification stage, we use a multi-branch network with a custom convolution module and a transformer module, including feature extraction, feature focus, and feature classification sub-networks. Feature extraction subnetworks extract the shallow features of the image and interact with the information through the convolution and transformer modules. Both the local and global features are extracted by the convolution module and transformer module of feature-focus subnetworks, and are classified by the feature classification subnetworks. The proposed network could decide whether or not a patient has pneumonia, and differentiate between Covid-19 and bacterial pneumonia. This network was implemented on the collected benchmark datasets and the result shows that accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score are 97.09%, 97.16%, 96.93%, and 97.04%, respectively. Our network was compared with other researchers' proposed methods and achieved better results in terms of accuracy, precision, and F1 score, proving that it is superior for Covid-19 detection. With further improvements to this network, we hope that it will provide doctors with an effective tool for diagnosing Covid-19.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Khan MA, Alhaisoni M, Nazir M, Alqahtani A, Binbusayyis A, Alsubai S, et al.. A Healthcare System for COVID19 Classification Using Multi-Type Classical Features Selection. Comput Mater Contin. 2023. Jan 4.
-
- Syed HH, Khan MA, Tariq U, Armghan A, Alenezi F, Khan JA, et al.. A Rapid Artificial Intelligence-Based Computer-Aided Diagnosis System for COVID-19 Classification from CT Images. Picconi B, editor. Behav Neurol [Internet]. 2021. Dec 27;2021:2560388. Available from: doi: 10.1155/2021/2560388 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. WHO: Statement on the second meeting of the international health regulations (2005) emergency committee regarding the outbreak of novel coronavirus (2019-ncov) (2020). functions. [Internet]. Available from: https://www.who.int/.
-
- World Health Organization. WHO: WHO director-general’s opening remarks at the media briefing on Covid-19 (2020). [Internet]. Available from: https://www.who.int.
-
- World Health Organization. WHO: Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Weekly Epidemiological Update and Weekly Operational Update, 2022. [Internet]. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

