Assessment of health staff's proficiency and quality of key malaria indicators in rural district of Ghana
- PMID: 36301986
- PMCID: PMC9612565
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274700
Assessment of health staff's proficiency and quality of key malaria indicators in rural district of Ghana
Abstract
Background: Routine Health Information Systems (RHIS) are important for not just sure enough control of malaria, but its elimination as well. If these systems are working, they can extensively provide accurate data on reported malaria cases instead of presenting modelled approximations of malaria burden. Queries are raised on both the quality and use of generated malaria data. Some issues of concern include inaccurate reporting of malaria cases as well as treatment plans, wrongly categorizing malaria cases in registers used to collate data and misplacing data or registers for reporting. This study analyses data quality concerning health staff's proficiency, timeliness, availability and data accuracy in the Sissala East Municipal Health Directorate (MHD).
Methods: A cross-sectional design was used to collect data from 15 facilities and 50 health staff members who offered clinical related care for malaria cases in the Sissala East MHD from 24th August 2020 to 17th September 2020. Fifteen health facilities were randomly selected from the 56 health facilities in the municipality that were implementing the malarial control programme, and they were included in the study.
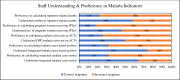
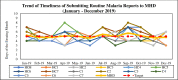
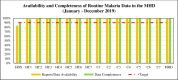
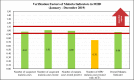
Results: On the question of when did staff receive any training on malaria-related health information management in the past six months prior to the survey, as minimal as 13 out of 50(26%) claimed to have been trained, whereas the majority 37 out of 50 (74%) had no training. In terms of proficiency in malaria indicators (MI), the majority (68% - 82%) of the respondents could not demonstrate the correct calculations of the indicators. Nevertheless, the MHD recorded monthly average timeliness of the 5th day [range: 4.7-5.7] within the reporting year. However, the MHD had a worse average performance of 5.4th and 5.7th days in July and September respectively. Furthermore, results indicated that 14 out of 15(93.3%) facilities exceeded the target to accomplish report availability (> = 90%) and data completeness (> = 90%). However, the verification factor (VF) of the overall malaria indicator showed that the MHD neither over-reported nor under-reported actual cases, with the corresponding level of data quality as Good (+/-5%).
Conclusions: The Majority of staff had not received any training on malaria-related RHIS. Some staff members did not know the correct definitions of some of MI used in the malaria programme, while the majority of them could not demonstrate the correct calculations of MI. Timeliness of reporting was below the target, nevertheless, copies of data that were submitted were available and completed. There should be training, supervision and monitoring to enhance staff proficiency and improve the quality of MI.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quality of routine malaria data captured at primary health facilities in the Hohoe Municipality, Ghana.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 4;15(1):4293. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78886-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39905148 Free PMC article.
-
A data quality assessment of the first four years of malaria reporting in the Senegal DHIS2, 2014-2017.BMC Health Serv Res. 2022 Jan 2;22(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-07364-6. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022. PMID: 34974837 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal and child health data quality in health care facilities at the Cape Coast Metropolis, Ghana.BMC Health Serv Res. 2022 Aug 30;22(1):1102. doi: 10.1186/s12913-022-08449-6. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022. PMID: 36042447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of immunization data quality of routine reports in Ho municipality of Volta region, Ghana.BMC Health Serv Res. 2020 Nov 4;20(1):1013. doi: 10.1186/s12913-020-05865-4. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020. PMID: 33148239 Free PMC article.
-
Fever case management at private health facilities and private pharmacies on the Kenyan coast: analysis of data from two rounds of client exit interviews and mystery client visits.Malar J. 2018 Mar 13;17(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12936-018-2267-8. Malar J. 2018. PMID: 29534750 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Quality of routine malaria data captured at primary health facilities in the Hohoe Municipality, Ghana.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 4;15(1):4293. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78886-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39905148 Free PMC article.
-
Coaching visits and supportive supervision for primary care facilities to improve malaria service data quality in Ghana: An intervention case study.PLOS Glob Public Health. 2025 Jun 6;5(6):e0003649. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0003649. eCollection 2025. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40478884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. (1993). Implementation of the global malaria control strategy: report of a WHO Study Group on the Implementation of the Global Plan of Action for Malaria Control 1993–2000 [meeting held in Geneva from 8 to 12 February 1993]. World Health Organization. - PubMed
-
- Lucas T. C., Nandi A. K., Keddie S. H., Chestnutt E. G., Howes R. E., Rumisha S. F., et al.. (2020). Improving disaggregation models of malaria incidence by ensembling non-linear models of prevalence. Spatial and Spatio-temporal Epidemiology, 100357. doi: 10.1016/j.sste.2020.100357 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Downie R. (2016). Sustaining Improvements to public health in Ethiopia. Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

