Unadjuvanted intranasal spike vaccine elicits protective mucosal immunity against sarbecoviruses
- PMID: 36302057
- PMCID: PMC9798903
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abo2523
Unadjuvanted intranasal spike vaccine elicits protective mucosal immunity against sarbecoviruses
Abstract
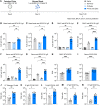
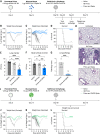
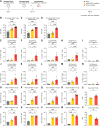
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic has highlighted the need for vaccines that not only prevent disease but also prevent transmission. Parenteral vaccines induce robust systemic immunity but poor immunity at the respiratory mucosa. We developed a vaccine strategy that we call "prime and spike," which leverages existing immunity generated by primary vaccination (prime) to elicit mucosal immune memory within the respiratory tract by using unadjuvanted intranasal spike boosters (spike). We show that prime and spike induces robust resident memory B and T cell responses, induces immunoglobulin A at the respiratory mucosa, boosts systemic immunity, and completely protects mice with partial immunity from lethal SARS-CoV-2 infection. Using divergent spike proteins, prime and spike enables the induction of cross-reactive immunity against sarbecoviruses.
Figures




Update of
-
Unadjuvanted intranasal spike vaccine booster elicits robust protective mucosal immunity against sarbecoviruses.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2022 Jan 26:2022.01.24.477597. doi: 10.1101/2022.01.24.477597. bioRxiv. 2022. Update in: Science. 2022 Nov 25;378(6622):eabo2523. doi: 10.1126/science.abo2523. PMID: 35118464 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Baden L. R., El Sahly H. M., Essink B., Kotloff K., Frey S., Novak R., Diemert D., Spector S. A., Rouphael N., Creech C. B., McGettigan J., Khetan S., Segall N., Solis J., Brosz A., Fierro C., Schwartz H., Neuzil K., Corey L., Gilbert P., Janes H., Follmann D., Marovich M., Mascola J., Polakowski L., Ledgerwood J., Graham B. S., Bennett H., Pajon R., Knightly C., Leav B., Deng W., Zhou H., Han S., Ivarsson M., Miller J., Zaks T., COVE Study Group , Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 403–416 (2021). 10.1056/NEJMoa2035389 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Emary K. R. W., Golubchik T., Aley P. K., Ariani C. V., Angus B., Bibi S., Blane B., Bonsall D., Cicconi P., Charlton S., Clutterbuck E. A., Collins A. M., Cox T., Darton T. C., Dold C., Douglas A. D., Duncan C. J. A., Ewer K. J., Flaxman A. L., Faust S. N., Ferreira D. M., Feng S., Finn A., Folegatti P. M., Fuskova M., Galiza E., Goodman A. L., Green C. M., Green C. A., Greenland M., Hallis B., Heath P. T., Hay J., Hill H. C., Jenkin D., Kerridge S., Lazarus R., Libri V., Lillie P. J., Ludden C., Marchevsky N. G., Minassian A. M., McGregor A. C., Mujadidi Y. F., Phillips D. J., Plested E., Pollock K. M., Robinson H., Smith A., Song R., Snape M. D., Sutherland R. K., Thomson E. C., Toshner M., Turner D. P. J., Vekemans J., Villafana T. L., Williams C. J., Hill A. V. S., Lambe T., Gilbert S. C., Voysey M., Ramasamy M. N., Pollard A. J., COVID-19 Genomics UK consortium, AMPHEUS Project, Oxford COVID-19 Vaccine Trial Group , Efficacy of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AZD1222) vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern 202012/01 (B.1.1.7): An exploratory analysis of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 397, 1351–1362 (2021). 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00628-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shah A. S. V., Gribben C., Bishop J., Hanlon P., Caldwell D., Wood R., Reid M., McMenamin J., Goldberg D., Stockton D., Hutchinson S., Robertson C., McKeigue P. M., Colhoun H. M., McAllister D. A., Effect of vaccination on transmission of SARS-CoV-2. N. Engl. J. Med. 385, 1718–1720 (2021). 10.1056/NEJMc2106757 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

