A Single Point Mutation Blocks the Entrance of Ligands to the Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor via the Lipid Bilayer
- PMID: 36302505
- PMCID: PMC9709915
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jcim.2c00865
A Single Point Mutation Blocks the Entrance of Ligands to the Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor via the Lipid Bilayer
Abstract
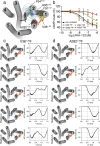
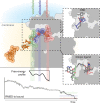
Molecular dynamic (MD) simulations have become a common tool to study the pathway of ligand entry to the orthosteric binding site of G protein-coupled receptors. Here, we have combined MD simulations and site-directed mutagenesis to study the binding process of the potent JWH-133 agonist to the cannabinoid CB2 receptor (CB2R). In CB2R, the N-terminus and extracellular loop 2 fold over the ligand binding pocket, blocking access to the binding cavity from the extracellular environment. We, thus, hypothesized that the binding pathway is a multistage process consisting of the hydrophobic ligand diffusing in the lipid bilayer to contact a lipid-facing vestibule, from which the ligand enters an allosteric site inside the transmembrane bundle through a tunnel formed between TMs 1 and 7 and finally moving from the allosteric to the orthosteric binding cavity. This pathway was experimentally validated by the Ala2827.36Phe mutation that blocks the entrance of the ligand, as JWH-133 was not able to decrease the forskolin-induced cAMP levels in cells expressing the mutant receptor. This proposed ligand entry pathway defines transient binding sites that are potential cavities for the design of synthetic modulators.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Allosteric and orthosteric pharmacology of cannabidiol and cannabidiol-dimethylheptyl at the type 1 and type 2 cannabinoid receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 May;176(10):1455-1469. doi: 10.1111/bph.14440. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 29981240 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and testing of novel classical cannabinoids: exploring the side chain ligand binding pocket of the CB1 and CB2 receptors.Bioorg Med Chem. 2003 Jul 17;11(14):3121-32. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(03)00238-4. Bioorg Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 12818675
-
A lipid pathway for ligand binding is necessary for a cannabinoid G protein-coupled receptor.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 4;285(23):17954-64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.041590. Epub 2010 Mar 10. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20220143 Free PMC article.
-
CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptor binding studies based on modeling and mutagenesis approaches.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2005 Jul;5(7):651-8. doi: 10.2174/1389557054368754. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 16026311 Review.
-
Cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptor ligand specificity and the development of CB2-selective agonists.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(14):1428-43. doi: 10.2174/092986708784567716. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18537620 Review.
Cited by
-
Computational approach for the evaluation of sesquiterpene lactone as a modulator of cannabinoid receptor type 2 for neurodegenerative disease prophylactics.Mol Divers. 2025 Apr 28. doi: 10.1007/s11030-025-11191-w. Online ahead of print. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 40293605
-
Multiple recent HCAR2 structures demonstrate a highly dynamic ligand binding and G protein activation mode.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 25;15(1):5364. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49536-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38918366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the endocannabinoid system: Structural determinants and molecular mechanism of allosteric modulation.Drug Discov Today. 2023 Jul;28(7):103615. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2023.103615. Epub 2023 May 11. Drug Discov Today. 2023. PMID: 37172889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Cannabinoid Receptor 2 (CB2) Low Lipophilicity Agonists Produce Distinct cAMP and Arrestin Signalling Kinetics without Bias.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 29;24(7):6406. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076406. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047385 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Applications of In Silico Approaches for Studying Receptor Mutations Associated with Human Pathologies.Molecules. 2024 Nov 13;29(22):5349. doi: 10.3390/molecules29225349. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39598735 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rasmussen S. G.; DeVree B. T.; Zou Y.; Kruse A. C.; Chung K. Y.; Kobilka T. S.; Thian F. S.; Chae P. S.; Pardon E.; Calinski D.; Mathiesen J. M.; Shah S. T.; Lyons J. A.; Caffrey M.; Gellman S. H.; Steyaert J.; Skiniotis G.; Weis W. I.; Sunahara R. K.; Kobilka B. K. Crystal structure of the beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex. Nature 2011, 477 (7366), 549–55. 10.1038/nature10361. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kang Y.; Zhou X. E.; Gao X.; He Y.; Liu W.; Ishchenko A.; Barty A.; White T. A.; Yefanov O.; Han G. W.; Xu Q.; de Waal P. W.; Ke J.; Tan M. H.; Zhang C.; Moeller A.; West G. M.; Pascal B. D.; Van Eps N.; Caro L. N.; Vishnivetskiy S. A.; Lee R. J.; Suino-Powell K. M.; Gu X.; Pal K.; Ma J.; Zhi X.; Boutet S.; Williams G. J.; Messerschmidt M.; Gati C.; Zatsepin N. A.; Wang D.; James D.; Basu S.; Roy-Chowdhury S.; Conrad C. E.; Coe J.; Liu H.; Lisova S.; Kupitz C.; Grotjohann I.; Fromme R.; Jiang Y.; Tan M.; Yang H.; Li J.; Wang M.; Zheng Z.; Li D.; Howe N.; Zhao Y.; Standfuss J.; Diederichs K.; Dong Y.; Potter C. S.; Carragher B.; Caffrey M.; Jiang H.; Chapman H. N.; Spence J. C.; Fromme P.; Weierstall U.; Ernst O. P.; Katritch V.; Gurevich V. V.; Griffin P. R.; Hubbell W. L.; Stevens R. C.; Cherezov V.; Melcher K.; Xu H. E. Crystal structure of rhodopsin bound to arrestin by femtosecond X-ray laser. Nature 2015, 523 (7562), 561–7. 10.1038/nature14656. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen Q.; Plasencia M.; Li Z.; Mukherjee S.; Patra D.; Chen C. L.; Klose T.; Yao X. Q.; Kossiakoff A. A.; Chang L.; Andrews P. C.; Tesmer J. J. G. Structures of rhodopsin in complex with G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 1. Nature 2021, 595 (7868), 600–605. 10.1038/s41586-021-03721-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

