Safety and Efficacy of Belimumab in Patients with Lupus Nephritis: Open-Label Extension of BLISS-LN Study
- PMID: 36302567
- PMCID: PMC9718049
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.02520322
Safety and Efficacy of Belimumab in Patients with Lupus Nephritis: Open-Label Extension of BLISS-LN Study
Abstract
Background and objectives: In the BLISS-LN study, belimumab improved kidney outcomes in adult patients with active lupus nephritis. This 28-week open-label extension of BLISS-LN assessed belimumab's safety and efficacy.
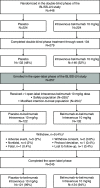
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Eligible patients completing BLISS-LN received monthly intravenous belimumab 10 mg/kg plus standard therapy. End points included safety, open-label week 28 primary efficacy renal response (urine protein-creatinine ratio [UPCR] ≤0.7, eGFR no more than 20% below open-label baseline value or ≥60 ml/min per 1.73 m2, no prohibited medications) and complete renal response (UPCR <0.5, eGFR no more than 10% below open-label baseline value or ≥90 ml/min per 1.73 m2, no prohibited medications), and UPCR and eGFR by visit. Responses were also analyzed post hoc using the double-blind phase criteria.
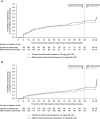
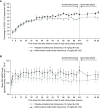
Results: Of 257 enrolled patients, 255 were treated (safety population: n=123 switched from placebo-to-belimumab; n=132 remained on belimumab); 245 (97%) patients completed the study. Adverse events and serious adverse events were experienced by 62% and 4% of placebo-to-belimumab patients, respectively, and by 70% and 8% of belimumab-to-belimumab patients, respectively. One death occurred in the placebo-to-belimumab group. From open-label baseline to week 28, increases occurred in the proportions of patients achieving primary efficacy renal response (placebo-to-belimumab: from 60% to 67%; belimumab-to-belimumab: from 70% to 75%) and complete renal response (placebo-to-belimumab: from 36% to 48%; belimumab-to-belimumab: from 48% to 62%). Based on double-blind phase criteria, changes also occurred in the proportions achieving primary efficacy renal response (placebo-to-belimumab: from 54% to 53%; belimumab-to-belimumab: from 66% to 52%) and complete renal response (placebo-to-belimumab: from 34% to 35%; belimumab-to-belimumab: from 46% to 41%). The seeming decrease in response rates in the belimumab-to-belimumab groups was attributed to discontinuations/administration of glucocorticoids for non-SLE reasons as opposed to nephritis. Median UPCR and eGFR values were similar at open-label baseline and week 28.
Conclusions: No new safety signals were identified, and efficacy was generally maintained throughout the open-label phase.
Clinical trial registry name and registration number: BLISS-LN, NCT01639339.
Keywords: belimumab; clinical trial; glomerular disease; glomerulonephritis; kidney disease; lupus nephritis; proteinuria.
Copyright © 2022 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

Comment in
-
The Role of Anti-B Cell Activating Factor Therapy for Treating Lupus Nephritis.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022 Nov;17(11):1583-1585. doi: 10.2215/CJN.11340922. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 36302568 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hanly JG, O’Keeffe AG, Su L, Urowitz MB, Romero-Diaz J, Gordon C, Bae SC, Bernatsky S, Clarke AE, Wallace DJ, Merrill JT, Isenberg DA, Rahman A, Ginzler EM, Fortin P, Gladman DD, Sanchez-Guerrero J, Petri M, Bruce IN, Dooley MA, Ramsey-Goldman R, Aranow C, Alarcón GS, Fessler BJ, Steinsson K, Nived O, Sturfelt GK, Manzi S, Khamashta MA, van Vollenhoven RF, Zoma AA, Ramos-Casals M, Ruiz-Irastorza G, Lim SS, Stoll T, Inanc M, Kalunian KC, Kamen DL, Maddison P, Peschken CA, Jacobsen S, Askanase A, Theriault C, Thompson K, Farewell V: The frequency and outcome of lupus nephritis: Results from an international inception cohort study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 55: 252–262, 2016. 10.1093/rheumatology/kev311 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker KP, Edwards BM, Main SH, Choi GH, Wager RE, Halpern WG, Lappin PB, Riccobene T, Abramian D, Sekut L, Sturm B, Poortman C, Minter RR, Dobson CL, Williams E, Carmen S, Smith R, Roschke V, Hilbert DM, Vaughan TJ, Albert VR: Generation and characterization of LymphoStat-B, a human monoclonal antibody that antagonizes the bioactivities of B lymphocyte stimulator. Arthritis Rheum 48: 3253–3265, 2003. 10.1002/art.11299 - DOI - PubMed
-
- European Medicines Agency : Belimumab Summary of Product Characteristics. Available at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/benlysta-epar.... Accessed January 10 2022
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

