Heme delivery to heme oxygenase-2 involves glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- PMID: 36302634
- PMCID: PMC9661526
- DOI: 10.1515/hsz-2022-0230
Heme delivery to heme oxygenase-2 involves glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Abstract
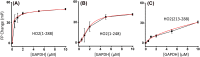
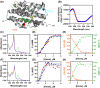
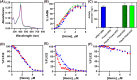
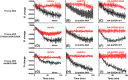
Heme regulatory motifs (HRMs) are found in a variety of proteins with diverse biological functions. In heme oxygenase-2 (HO2), heme binds to the HRMs and is readily transferred to the catalytic site in the core of the protein. To further define this heme transfer mechanism, we evaluated the ability of GAPDH, a known heme chaperone, to transfer heme to the HRMs and/or the catalytic core of HO2. Our results indicate GAPDH and HO2 form a complex in vitro. We have followed heme insertion at both sites by fluorescence quenching in HEK293 cells with HO2 reporter constructs. Upon mutation of residues essential for heme binding at each site in our reporter construct, we found that HO2 binds heme at the core and the HRMs in live cells and that heme delivery to HO2 is dependent on the presence of GAPDH that is competent for heme binding. In sum, GAPDH is involved in heme delivery to HO2 but, surprisingly, not to a specific site on HO2. Our results thus emphasize the importance of heme binding to both the core and the HRMs and the interplay of HO2 with the heme pool via GAPDH to maintain cellular heme homeostasis.
Keywords: GAPDH; chaperone; glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; heme oxygenase-2; heme regulatory motifs; heme trafficking.
© 2022 Walter de Gruyter GmbH, Berlin/Boston.
Figures

References
-
- Adams S.R., Campbell R.E., Gross L.A., Martin B.R., Walkup G.K., Yao Y., Llopis J., Tsien R.Y. New biarsenical ligands and tetracysteine motifs for protein labeling in vitro and in vivo: synthesis and biological applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002;124:6063–6076. doi: 10.1021/ja017687n. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bagai I., Sarangi R., Fleischhacker A.S., Sharma A., Hoffman B.M., Zuiderweg E.R.P., Ragsdale S.W. Spectroscopic studies reveal that the heme regulatory motifs of heme oxygenase-2 are dynamically disordered and exhibit redox-dependent interaction with heme. Biochemistry. 2015;54:2693–2708. doi: 10.1021/bi501489r. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
