Quantitative sequencing using BID-seq uncovers abundant pseudouridines in mammalian mRNA at base resolution
- PMID: 36302989
- PMCID: PMC10017504
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-022-01505-w
Quantitative sequencing using BID-seq uncovers abundant pseudouridines in mammalian mRNA at base resolution
Abstract
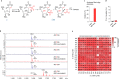
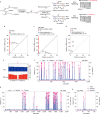
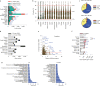
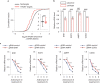
Functional characterization of pseudouridine (Ψ) in mammalian mRNA has been hampered by the lack of a quantitative method that maps Ψ in the whole transcriptome. We report bisulfite-induced deletion sequencing (BID-seq), which uses a bisulfite-mediated reaction to convert pseudouridine stoichiometrically into deletion upon reverse transcription without cytosine deamination. BID-seq enables detection of abundant Ψ sites with stoichiometry information in several human cell lines and 12 different mouse tissues using 10-20 ng input RNA. We uncover consensus sequences for Ψ in mammalian mRNA and assign different 'writer' proteins to individual Ψ deposition. Our results reveal a transcript stabilization role of Ψ sites installed by TRUB1 in human cancer cells. We also detect the presence of Ψ within stop codons of mammalian mRNA and confirm the role of Ψ in promoting stop codon readthrough in vivo. BID-seq will enable future investigations of the roles of Ψ in diverse biological processes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
C.H. is a scientific founder, a member of the scientific advisory board and equity holder of Aferna Green, Inc. and AccuaDX Inc., and a scientific cofounder and equity holder of Accent Therapeutics, Inc.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

