AGO1 and HSP90 buffer different genetic variants in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 36303325
- PMCID: PMC9910400
- DOI: 10.1093/genetics/iyac163
AGO1 and HSP90 buffer different genetic variants in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
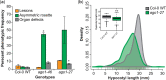
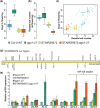
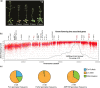
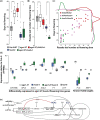
Argonaute 1 (AGO1), the principal protein component of microRNA-mediated regulation, plays a key role in plant growth and development. AGO1 physically interacts with the chaperone HSP90, which buffers cryptic genetic variation in plants and animals. We sought to determine whether genetic perturbation of AGO1 in Arabidopsis thaliana would also reveal cryptic genetic variation, and if so, whether AGO1-dependent loci overlap with those dependent on HSP90. To address these questions, we introgressed a hypomorphic mutant allele of AGO1 into a set of mapping lines derived from the commonly used Arabidopsis strains Col-0 and Ler. Although we identified several cases in which AGO1 buffered genetic variation, none of the AGO1-dependent loci overlapped with those buffered by HSP90 for the traits assayed. We focused on 1 buffered locus where AGO1 perturbation uncoupled the traits days to flowering and rosette leaf number, which are otherwise closely correlated. Using a bulk segregant approach, we identified a nonfunctional Ler hua2 mutant allele as the causal AGO1-buffered polymorphism. Introduction of a nonfunctional hua2 allele into a Col-0 ago1 mutant background recapitulated the Ler-dependent ago1 phenotype, implying that coupling of these traits involves different molecular players in these closely related strains. Taken together, our findings demonstrate that even though AGO1 and HSP90 buffer genetic variation in the same traits, these robustness regulators interact epistatically with different genetic loci, suggesting that higher-order epistasis is uncommon. Plain Language Summary Argonaute 1 (AGO1), a key player in plant development, interacts with the chaperone HSP90, which buffers environmental and genetic variation. We found that AGO1 buffers environmental and genetic variation in the same traits; however, AGO1-dependent and HSP90-dependent loci do not overlap. Detailed analysis of a buffered locus found that a nonfunctional HUA2 allele decouples days to flowering and rosette leaf number in an AGO1-dependent manner, suggesting that the AGO1-dependent buffering acts at the network level.
Keywords: AGO1; HSP90; HUA2; Plant Genetics and Genomics; buffering; capacitors; epistasis.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Genetics Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Andrés F, Coupland G.. The genetic basis of flowering responses to seasonal cues. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13(9):627–639. - PubMed
-
- Axtell MJ. Classification and comparison of small RNAs from plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2013;64:137–159. - PubMed
-
- Bloomer RH, Dean C.. Fine-tuning timing: natural variation informs the mechanistic basis of the switch to flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot. 2017;68(20):5439–5452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

