Disruption of white matter integrity and its relationship with cognitive function in non-severe traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 36303559
- PMCID: PMC9592834
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1011304
Disruption of white matter integrity and its relationship with cognitive function in non-severe traumatic brain injury
Abstract
Background: Impairment in cognitive function is a recognized outcome of traumatic brain injury (TBI). However, the degree of impairment has variable relationship with TBI severity and time post injury. The underlying pathology is often due to diffuse axonal injury that has been found even in mild TBI. In this study, we examine the state of white matter putative connectivity in patients with non-severe TBI in the subacute phase, i.e., within 10 weeks of injury and determine its relationship with neuropsychological scores.
Methods: We conducted a case-control prospective study involving 11 male adult patients with non-severe TBI and an age-matched control group of 11 adult male volunteers. Diffusion MRI scanning and neuropsychological tests were administered within 10 weeks post injury. The difference in fractional anisotropy (FA) values between the patient and control groups was examined using tract-based spatial statistics. The FA values that were significantly different between patients and controls were then correlated with neuropsychological tests in the patient group.
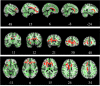
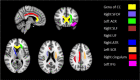
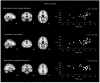
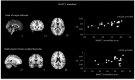
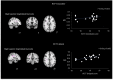
Results: Several clusters with peak voxels of significant FA reductions (p < 0.05) in the white matter skeleton were seen in patients compared to the control group. These clusters were located in the superior fronto-occipital fasciculus, superior longitudinal fasciculus, uncinate fasciculus, and cingulum, as well as white matter fibers in the area of genu of corpus callosum, anterior corona radiata, superior corona radiata, anterior thalamic radiation and part of inferior frontal gyrus. Mean global FA magnitude correlated significantly with MAVLT immediate recall scores while matrix reasoning scores correlated positively with FA values in the area of right superior fronto-occipital fasciculus and left anterior corona radiata.
Conclusion: The non-severe TBI patients had abnormally reduced FA values in multiple regions compared to controls that correlated with several measures of executive function during the sub-acute phase of TBI.
Keywords: diffusion MRI; fractional anisotropy; neuropsychological test; tract-based spatial statistic; traumatic brain injury.
Copyright © 2022 Abdullah, Ahmad, Zakaria, Tamam, Abd Hamid, Chai, Omar, Abdul Rahman, Fitzrol, Idris, Ghani, Wan Mohamad, Mustafar, Hanafi, Reza, Umar, Mohd Zulkifly, Ang, Zakaria, Musa, Othman, Embong, Sapiai, Kandasamy, Ibrahim, Abdullah, Amaruchkul, Valdes-Sosa, Bringas Vega, Biswal, Songsiri, Yaacob, Sumari, Noh, Azman, Jamir Singh and Abdullah.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Frieden TR, Houry D, Baldwin G. Report to congress on traumatic brain injury in the United States: epidemiology and rehabilitation. (2015). Available online at: https://www.cdc.gov/traumaticbraininjury/pdf/tbi_report_to_congress_epi_... (accessed July 04 2022).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

