Valorization of agricultural wastes for biofuel applications
- PMID: 36303926
- PMCID: PMC9593297
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11117
Valorization of agricultural wastes for biofuel applications
Abstract
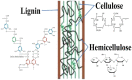
Continuous environmental degradation, volatility in the oil market, and unimpressive functioning of fossil-based (FB) fuels in compression ignition engines have expanded the tempo of the search for alternative fuels. Due to the astronomical rise in global population, improved agricultural, commercial, and manufacturing activities, enhanced farming and other food production and utilization ventures, agricultural waste generation, renewable fuel consumption, and emission of toxic gases. The need for cost-effective, readily available, and environmentally benign agricultural waste to biofuels has never been more crucial. Biofuels are renewable, biodegradable, low-cost, and eco-friendly fuels that are produced by microorganisms from waste lignocellulosic biomass. Conversion of agricultural wastes to biofuel does not exacerbate food security, contributes to waste management, prevents environmental degradation, and ensures energy security. This study reviews the conversion of agricultural wastes into biofuels with special emphasis on bioethanol, biohydrogen, biobutanol, biomethane, biomethanol, and biodiesel for various applications. It is safe to conclude that wastes generated from agricultural activities and processes are useful and can be harnessed to meet the affordable and accessible global renewable energy target. The result of this investigation will improve the body of knowledge and provide novel strategies and pathways for the utilization of agricultural wastes. Going forward, more collaborative and interdisciplinary studies are required to evolve state-of-the-art, ecofriendly, and cost-effective conversion pathways for agricultural wastes to promote the utilization of the generated renewable fuels. More human, financial, and infrastructural investments are desirable to motivate the conversion of agricultural waste into biofuels to ensure environmental sanitation and sustainability, promote renewable fuel utilization, and avert the raging implosion of our planet.
Keywords: Agricultural wastes; Biofuel; Biomethane; Lignocellulosic biomass; Waste conversion.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Simultaneous production of biofuel from agricultural wastes and bioremediation of the waste substrates: A review.Curr Res Microb Sci. 2024 Nov 15;7:100305. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2024.100305. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Microb Sci. 2024. PMID: 39620096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utilization of agricultural waste biomass and recycling toward circular bioeconomy.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Jan;30(4):8526-8539. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-20669-1. Epub 2022 May 13. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 35554831 Review.
-
A mini review on renewable sources for biofuel.Bioresour Technol. 2014 Oct;169:742-749. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.07.022. Epub 2014 Jul 11. Bioresour Technol. 2014. PMID: 25115598 Review.
-
Biofuel production for circular bioeconomy: Present scenario and future scope.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Jul 20;935:172863. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.172863. Epub 2024 May 23. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 38788387 Review.
-
Anaerobic Digestion of Agri-Food Wastes for Generating Biofuels.Indian J Microbiol. 2021 Dec;61(4):427-440. doi: 10.1007/s12088-021-00977-9. Epub 2021 Aug 30. Indian J Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34744198 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biobutanol production from underutilized substrates using Clostridium: Unlocking untapped potential for sustainable energy development.Curr Res Microb Sci. 2024 Jun 8;7:100250. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2024.100250. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Microb Sci. 2024. PMID: 38974669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrothermal Liquefaction: How the Holistic Approach by Nature Will Help Solve the Environmental Conundrum.Molecules. 2023 Dec 16;28(24):8127. doi: 10.3390/molecules28248127. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomedical potential of agricultural waste extracts: phytochemicals with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and anti-parasitic activities.3 Biotech. 2025 Jul;15(7):231. doi: 10.1007/s13205-025-04407-1. Epub 2025 Jul 1. 3 Biotech. 2025. PMID: 40612585
-
Enhanced Production of Prodigiosin Utilizing Agro-industrial Yellow Mustard Cake Waste by a Novel Strain Serratia marcescens SBL03.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025 Aug;197(8):5131-5147. doi: 10.1007/s12010-025-05259-4. Epub 2025 May 23. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40408012
-
Optimization of the Microwave-Assisted Extraction Conditions for Phenolic Compounds from Date Seeds.Foods. 2024 Nov 25;13(23):3771. doi: 10.3390/foods13233771. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39682843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adeyemi M., Olatubosun R., Babarinde O., Omale P. Comparative study of bioethanol production from wheat straw and rice straw. J. Chem Soc. Nigeria. 2019;44(2):301–309.
-
- Aggarangsi P., Moran J., Koonaphapdeelert S., Tippayawong N. Performance comparison of biomethane, natural gas and gasoline in powering a pickup truck. Biofuels. 2022:1–8.
-
- Ahou Y.S., Bautista Angeli J.-R., Awad S., Baba-Moussa L., Andres Y. Lab-scale anaerobic digestion of cassava peels: the first step of energy recovery from cassava waste and water hyacinth. Environ. Technol. 2021;42(9):1438–1451. - PubMed
-
- Alternative Fuels Data Center Biobutanol. 2021 https://afdc.energy.gov/fuels/emerging_biobutanol.html
-
- Anitha M., Kamarudin S., Shamsul N., Kofli N. Determination of bio-methanol as intermediate product of anaerobic co-digestion in animal and agriculture wastes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2015;40(35):11791–11799.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

