Development of Gram Stain Scoring System Based on Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in the Sheep Model for Testing Toxicity of Vaginal Products
- PMID: 36304006
- PMCID: PMC9580737
- DOI: 10.3389/frph.2021.714798
Development of Gram Stain Scoring System Based on Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in the Sheep Model for Testing Toxicity of Vaginal Products
Abstract
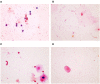
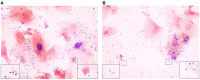
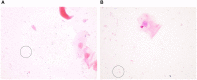
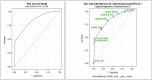
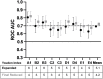
Background: Development of safe, effective products to prevent the sexual transmission of HIV remains a priority. Prior to clinical testing, the products must undergo strict safety evaluations to avoid mucosal drug toxicity, inflammation, and vaginal microbiome (VMB) shifts. Based on the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) guidance, we designed a study to measure the inflammatory markers and VMB changes after intravaginal treatment with products that have been associated with toxicity, with the objective to develop a Gram stain slide scoring system, similar to Nugent scoring, correlated with the proinflammatory cytokines in sheep. Methods: Non-pregnant Dorset ewes (n = 34) were randomized to receive 5 ml intravaginal 4% nonoxynol-9 (N9) contraceptive gel, positive control (0.2% benzalkonium chloride), placebo control [hydroxethyl cellulose (HEC)], or no application daily for 10 days, with 11-day post-treatment follow-up. The vaginal swabs were collected for the cytokines, VMB, and Gram-stained slides. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) analysis of cytokines interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-8, CXCL10, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) was used to determine inflammatory state of the sample. Vaginal microbiome community types (CT) were utilized to create five equivalent slide subsets for iterative development of a Gram-stained slide scoring system with comparisons with inflammatory state based on the cytokine levels. Results: Digital images of the Gram-stained slides were scored based on Gram staining and morphology of bacteria, presence of sheep epithelial cells, and immune cells. The scoring system was modified in an iterative fashion with weighting based on cytokine categorization of inflamed samples, with three of four cytokine values above the mean indicating that the sample was inflamed. The parameters in the final version of the scoring system included mature epithelial cells, Gram-negative rods, and Gram-positive diplococci indicating normal and immune cells indicating inflammation. The area under the receiver operator characteristic curve (ROC AUC) was 0.725 (ROC AUCs range between 0.5 and 1.0) with a greater area indicating higher diagnostic ability of a test with a binary outcome: inflamed or normal. Conclusion: The scoring system, derived from the advanced VMB and cytokine analyses, provides a validated, practical method for quantification of Gram-stained slides that can be performed in most laboratories, increasing the potential for standardization. The training plan can assist laboratories to determine the safety of intravaginal products in their sheep studies or the methodological approach can be applied to other animal models where such data are also needed.
Keywords: Gram stain scoring system; intravaginal drug delivery; ovine sheep vaginal model; proinflammatory cytokines; toxicity testing; vaginal microbiome.
Copyright © 2021 Vincent, Miller, Maxwell, Richardson-Harman, O'Neill, Dawson, Madsen, Walker, Swartz and Pyles.
Conflict of interest statement
NR-H is employed by Alpha StatConsult, LLC. GS, CO'N, and CW were employed by Advanced Bioscience Laboratories, Inc. RP and KV were paid consultants to Advanced Bioscience Laboratories, Inc., under a contract with NIH (as shown in Funding). TM is employed by Sinclair Research Center. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of the Ovine Vaginal Microbiome and Inflammation Patterns as an Improved Testing Model of Human Vaginal Irritation.Front Reprod Health. 2021 Dec 7;3:714829. doi: 10.3389/frph.2021.714829. eCollection 2021. Front Reprod Health. 2021. PMID: 36303974 Free PMC article.
-
Establishing a Th17 based mouse model for preclinical assessment of the toxicity of candidate microbicides.Chin Med J (Engl). 2010 Dec;123(23):3381-8. Chin Med J (Engl). 2010. PMID: 22166518
-
Preclinical evaluation of a dual-acting microbicidal prodrug WHI-07 in combination with vanadocene dithiocarbamate in the female reproductive tract of rabbit, pig, and cat.Toxicol Pathol. 2007 Dec;35(7):910-27. doi: 10.1080/01926230701748115. Toxicol Pathol. 2007. PMID: 18098038
-
Clinical development of microbicides for the prevention of HIV infection.Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10(3):315-36. doi: 10.2174/1381612043386374. Curr Pharm Des. 2004. PMID: 14754390 Review.
-
Development, validation and implementation of an in vitro model for the study of metabolic and immune function in normal and inflamed human colonic epithelium.Dan Med J. 2015 Jan;62(1):B4973. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25557335 Review.
Cited by
-
Next generation 3D-printed intravaginal ring for prevention of HIV and unintended pregnancy.Biomaterials. 2023 Oct;301:122260. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122260. Epub 2023 Aug 3. Biomaterials. 2023. PMID: 37549505 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vincent KL, Bell BA, Rosenthal SL, Bourne N, Patton DL, Cosgrove Sweeney YT, et al. . Application of optical coherence tomography for monitoring changes in cervicovaginal epithelial morphology in macaques: potential for assessment of microbicide safety. Sex Transm Dis. (2008) 35:269–75. 10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31815abad8 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

