Ovarian Fragmentation and AKT Stimulation for Expansion of Fertile Lifespan
- PMID: 36304045
- PMCID: PMC9580792
- DOI: 10.3389/frph.2021.636771
Ovarian Fragmentation and AKT Stimulation for Expansion of Fertile Lifespan
Abstract
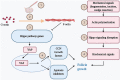
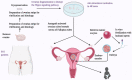
Since the first baby was born after in vitro fertilization, the female infertility treatment has been well-developed, yielding successful outcomes. However, successful pregnancies for patients with premature ovarian insufficiency and diminished ovarian reserve are still difficult and diverse therapies have been suggested to improve the chances to have their genetically linked offspring. Recent studies demonstrated that the activation Akt pathway by using a phosphatase and tensin homolog enzyme inhibitor and a phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase stimulator can activate dormant primordial follicles in both mice and human ovaries. Subsequent researches suggested that the disruption of Hippo signaling pathway by ovarian fragmentation increased the expression of downstream growth factors and secondary follicle growth. Based on the combination of ovarian fragmentation and Akt stimulation, the in vitro activation (IVA) approach has resulted in successful follicle growth and live births in premature ovarian insufficiency patients. The approach with disruption of Hippo signaling only was also shown to be effective for treating poor ovarian responders with diminishing ovarian reserve, including advanced age women and cancer patients undergoing sterilizing treatments. This review aims to summarize the effectiveness of ovarian fragmentation and Akt stimulation on follicle growth and the potential of IVA in extending female fertile lifespan.
Keywords: Akt stimulation; diminished ovarian reserve; in vitro activation; ovarian fragmentation; premature ovarian insufficiency.
Copyright © 2021 Vo and Kawamura.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Successful fertility preservation following ovarian tissue vitrification in patients with primary ovarian insufficiency.Hum Reprod. 2015 Mar;30(3):608-15. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deu353. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Hum Reprod. 2015. PMID: 25567618
-
Activation of dormant follicles: a new treatment for premature ovarian failure?Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Jun;28(3):217-22. doi: 10.1097/GCO.0000000000000268. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2016. PMID: 27022685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hippo signaling disruption and Akt stimulation of ovarian follicles for infertility treatment.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Oct 22;110(43):17474-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1312830110. Epub 2013 Sep 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24082083 Free PMC article.
-
Hippo signaling disruption and ovarian follicle activation in infertile patients.Fertil Steril. 2020 Sep;114(3):458-464. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2020.07.031. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Fertil Steril. 2020. PMID: 32782158 Review.
-
Dynamics of PI3K and Hippo signaling pathways during in vitro human follicle activation.Hum Reprod. 2018 Sep 1;33(9):1705-1714. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dey250. Hum Reprod. 2018. PMID: 30032281
Cited by
-
Current Status of In Vitro Oocyte Growth and Development in Mammals.Reprod Med Biol. 2025 Jul 17;24(1):e12669. doi: 10.1002/rmb2.12669. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Reprod Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40678565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic chips in female reproduction: a systematic review of status, advances, and challenges.Theranostics. 2024 Jul 15;14(11):4352-4374. doi: 10.7150/thno.97301. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39113805 Free PMC article.
-
Oocyte aging in comparison to stem cells in mice.Front Aging. 2023 Apr 11;4:1158510. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2023.1158510. eCollection 2023. Front Aging. 2023. PMID: 37114094 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

