Manufacturing processes of peanut (Arachis hypogaea) allergen powder-dnfp
- PMID: 36304076
- PMCID: PMC9592818
- DOI: 10.3389/falgy.2022.1004056
Manufacturing processes of peanut (Arachis hypogaea) allergen powder-dnfp
Abstract
Background: Important components of drug safety, efficacy, and acceptability involve manufacturing and testing of the drug substance and drug product. Peanut flour sourcing/processing and manufacturing processes may affect final drug product allergen potency and contamination level, possibly impacting drug safety, quality, and efficacy. We describe key steps in the manufacturing processes of peanut (Arachis hypogaea) allergen powder-dnfp (PTAH; Palforzia®), a drug used in oral immunotherapy (OIT) for the treatment of peanut allergy.
Methods: Established criteria for source material must be met for manufacturing PTAH drug product. Degree of roasting was determined with a Hunter colorimeter. Protein/allergen content, identity, potency, safety, and quality of each batch of PTAH drug substance were assessed with a combustion analyzer, allergen-specific Western blot (immunoblotting), ELISA, and HPLC. Contaminants (ie, aflatoxin) were measured by UPLC.
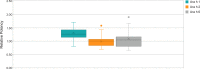
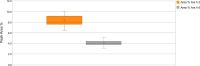
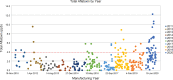
Results: Roasting degree beyond "light roast" was associated with variable degrees of protein allergen degradation, or potentially aggregation. Relative potency and amounts of protein allergens showed variability due in part to seasonal/manufacturing variability. Proportion of lots not meeting aflatoxin limits has increased in recent years. Up to 60% of peanut flour source material failed to meet screening selection acceptance criteria for proceeding to drug substance testing, mostly because of failure to meet potency acceptance criteria. Other lots were rejected due to safety (ie, aflatoxin) and quality. Influence of potency variation, within specification parameters, on safety/tolerability observed in trials was considered low, in part due to stringent controls placed at each step of manufacturing.
Conclusions: Extensive variability in allergen potency is a critical issue during immunotherapy, particularly during OIT initial dose escalation and up-dosing, as it may result in lack of efficacy or avoidable adverse allergic reactions. Based on EU and US regulatory requirements, the production of PTAH includes manufacturing controls to ensure drug product safety, potency, and quality. For example, although PTAH contains all peanut allergens, each lot has met strict criteria ensuring consistent allergenic potency of Ara h 1, Ara h 2, and Ara h 6. The rigor of PTAH's manufacturing process ensures reliable dose consistency and stability throughout its shelf life.
Keywords: drug; food; manufacturing; oral immunotherapy; peanut (Arachis hypogaea) allergen powder-dnfp; peanut allergy; standardization.
© 2022 Leonard, Ogawa, Jedrzejewski, Maleki, Chapman, Tilles, Du Toit, Mustafa and Vickery.
Conflict of interest statement
Stephanie A. Leonard reports being a consultant for Aimmune Therapeutics, a Nestlé Health Science company, DBV Technologies, and Cour Pharmaceuticals Development Co., Inc, a member of the International FPIES Association medical advisory board, a speaker for Aimmune Therapeutics, a Nestlé Health Science company, and a site investigator for Aimmune Therapeutics, a Nestlé Health Science company, and DBV Technologies. Yasushi Ogawa is an employee of Aimmune Therapeutics, a Nestlé Health Science company. Paul T. Jedrzejewski is an employee of Aimmune Therapeutics, a Nestlé Health Science company. Soheila J. Maleki has no disclosures to report. Martin D. Chapman reports an R01 research grant on the structural biology of allergens from NIH NIAID. In addition, they report honorarium for molecular allergology symposium from Johns Hopkins University and is a co-owner and shareholder of InBio. Stephen A. Tilles is an employee of Aimmune Therapeutics, a Nestlé Health Science company. George Du Toit reports research grants to their institution and advisory board fees from Aimmune Therapeutics, a Nestlé Health Science company. S. Shahzad Mustafa reports honoraria for Aimmune program. Brian P. Vickery reports advisory board/consultant for Aimmune Therapeutics, AllerGenis, FARE, Reacta; site investigator for Aimmune Therapeutics, a Nestlé Health Science company, DBV, Genentech, Regeneron; and research grants from FARE and NIAID.
Figures


References
-
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, Center for Veterinary Medicine, Office of Regulatory Affairs. Guidance for industry, quality systems approach to pharmaceutical CGMP regulations (2006). Available at: https://www.fda.gov/media/71023/download (Accessed May 19, 2022).
-
- United States Food and Drug Administration, Department of Health and Human Services. CFR - code of federal regulations title 21, 21CFR314.3 (2022). Available at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/cfrsearch.cfm?f... (Accessed May 19, 2022).
-
- United States Food and Drug Administration, Department of Health and Human Services. CFR - code of federal regulations title 21, 21CFR101.14 (2022). Available at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/cfrsearch.cfm?f... (Accessed May 19, 2022).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

