Cytological Grading of Breast Carcinomas and Its Prognostic Implications
- PMID: 36304360
- PMCID: PMC9585361
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.29385
Cytological Grading of Breast Carcinomas and Its Prognostic Implications
Abstract
Introduction Determining the histological grade of breast carcinomas before mastectomy is necessary to decide about neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Core needle biopsies used for this purpose often under-grade the tumour. The grade obtained from fine needle aspiration cytology samples will help in such situations and whenever biopsy is not done, as in a resource-poor setup. Many studies are being done to find out the cytological grading system that correlates well with histological grading. Methods This study was done between 2016 and 2019 including the cases in which both modified radical mastectomy and fine needle aspiration of the tumour had been done. Robinson's cytological grading was done in Papanicolaou and haematoxylin & eosin (H&E) stained cytology smears and correlated with modified Bloom-Richardson histologic grading done in modified radical mastectomy specimens. We also studied the prognostic significance of Robinson's method by studying the association between cytological grade and lymph node metastasis. Results Sixty cases were studied. The two methods had the same grade in 49 (81.7%) cases. They showed a significant positive correlation (Spearman correlation coefficient 0.848, p-0.0001), significant association (Chi-square test, p-0.0001), and substantial agreement (kappa value 0.72). Multiple regression analysis showed chromatin score and nucleoli score as the most influential parameters. Lymph node metastasis showed significant association with cytological grade (p-0.0003), cell dissociation score (p-0.0001), nucleoli score (p-0.01), and chromatin score (p-0.04). Conclusion Robinson's cytological grading is a simple, reliable adjunct/alternative to core needle biopsies for grading breast carcinomas before mastectomy. Hence, it can be made a part of routine cytology reporting of breast carcinomas. Further long-term studies will help in confirming its prognostic significance.
Keywords: breast cancer; breast carcinoma; core needle biopsy; cytological grading; fine needle aspiration cytology; histological grading.
Copyright © 2022, Rajendran et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
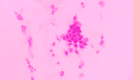
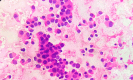
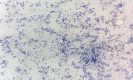
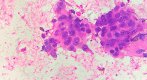
Figures

Similar articles
-
Correlative Study of Cytological Features in Grading of Invasive Breast Carcinoma.J Cytol. 2018 Jul-Sep;35(3):149-152. doi: 10.4103/JOC.JOC_2_18. J Cytol. 2018. PMID: 30089943 Free PMC article.
-
Robinson's cytological grading on aspirates of breast carcinoma: Correlation with Bloom Richardson's histological grading.J Cytol. 2009 Oct;26(4):140-3. doi: 10.4103/0970-9371.62182. J Cytol. 2009. PMID: 21938177 Free PMC article.
-
Correlative Evaluation of Seven Cytological 3-Tier Grading Systems of Breast Carcinoma with the Standard Histological Grading: A 4 and ½ Year Study.Acta Cytol. 2023;67(5):482-492. doi: 10.1159/000531463. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Acta Cytol. 2023. PMID: 37331335
-
Grading systems in the cytological diagnosis of breast cancer: a review.J Cancer Res Ther. 2014 Oct-Dec;10(4):839-45. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.140979. J Cancer Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25579516 Review.
-
Diagnostic value of fine needle aspirates processed by ThinPrep® for the assessment of axillary lymph node status in patients with invasive carcinoma of the breast.Cytopathology. 2013 Dec;24(6):372-6. doi: 10.1111/cyt.12022. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Cytopathology. 2013. PMID: 23020285 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of machine learning-based malignant pericardial effusion-related model in breast cancer: Implications for clinical significance, tumor immune and drug-therapy.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 2;10(5):e27507. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27507. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38463870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Histologic grade remains a prognostic factor for breast cancer regardless of the number of positive lymph nodes and tumor size: a study of 161 708 cases of breast cancer from the SEER Program. Schwartz AM, Henson DE, Chen D, Rajamarthandan S. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2014;138:1048–1052. - PubMed
-
- The reliability of histological grade in breast cancer core needle biopsies depends on biopsy size: a comparative study with subsequent surgical excisions. Focke CM, Decker T, van Diest PJ. Histopathology. 2016;69:1047–1054. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
