Machine Learning Analyses Reveal Circadian Features Predictive of Risk for Sleep Disturbance
- PMID: 36304418
- PMCID: PMC9595061
- DOI: 10.2147/NSS.S379888
Machine Learning Analyses Reveal Circadian Features Predictive of Risk for Sleep Disturbance
Abstract
Introduction: Sleep disturbances often co-occur with mood disorders, with poor sleep quality affecting over a quarter of the global population. Recent advances in sleep and circadian biology suggest poor sleep quality is linked to disruptions in circadian rhythms, including significant associations between sleep features and circadian clock gene variants.
Methods: Here, we employ machine learning techniques, combined with statistical approaches, in a deeply phenotyped population to explore associations between clock genotypes, circadian phenotypes (diurnal preference and circadian phase), and risk for sleep disturbance symptoms.
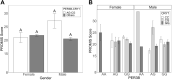
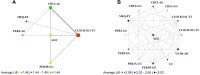
Results: As found in previous studies, evening chronotypes report high levels of sleep disturbance symptoms. Using molecular chronotyping by measuring circadian phase, we extend these findings and show that individuals with a mismatch between circadian phase and diurnal preference report higher levels of sleep disturbance. We also report novel synergistic interactions in genotype combinations of Period 3, Clock and Cryptochrome variants (PER3B (rs17031614)/ CRY1 (rs228716) and CLOCK3111 (rs1801260)/ CRY2 (rs10838524)) that yield strong associations with sleep disturbance, particularly in males.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that both direct and indirect mechanisms may impact sleep quality; sex-specific clock genotype combinations predictive of sleep disturbance may represent direct effects of clock gene function on downstream pathways involved in sleep physiology. In addition, the mediation of clock gene effects on sleep disturbance indicates circadian influences on the quality of sleep. Unraveling the complex molecular mechanisms at the intersection of circadian and sleep physiology is vital for understanding how genetic and behavioral factors influencing circadian phenotypes impact sleep quality. Such studies provide potential targets for further study and inform efforts to improve non-invasive therapeutics for sleep disorders.
Keywords: chronotype; circadian clock; circadian misalignment; machine learning; sleep disturbance; sleep quality.
© 2022 Overton et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

