Describing immune factors associated with Hepatitis B surface antigen loss: A nested case-control study of a Chinese sample from Wuwei City
- PMID: 36304473
- PMCID: PMC9592898
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1025654
Describing immune factors associated with Hepatitis B surface antigen loss: A nested case-control study of a Chinese sample from Wuwei City
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) loss is considered a functional cure for chronic hepatitis B (CHB), however, several factors influence HBsAg loss.
Methods: 29 CHB patients who had achieved HBsAg loss, were selected and 58 CHB patients with persistent HBsAg were matched, according to gender and age (+/- 3 years). Logistic regression and restricted cubic spline (RCS) modelling were performed.
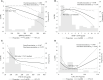
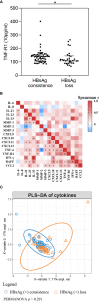
Results: Multivariate-adjusted logistic regression, based on stepwise selection, showed that baseline HBsAg levels negatively correlated with HBsAg loss (odds ratio [OR] = 0.99, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.98-0.99). Interferon treatment positively related with HBsAg loss (OR = 7.99, 95%CI = 1.62-44.88). After adjusting for age, HBsAg level, ALT level, HBeAg status and interferon treatment, MMP-1 (OR = 0.66, 95%CI = 0.44-0.97), CXCL9 (OR = 0.96, 95%CI = 0.93-0.99) and TNF-R1 (OR = 0.97, 95%CI = 0.94-0.99) baseline levels all negatively correlated with HBsAg loss. Our multivariate-adjusted RCS model showed that baseline CXCL10 was associated with HBsAg loss although the relationship was "U-shaped".
Conclusions: Cytokines such as MMP-1, CXCL9, CXCL10 and TNF-R1 are important factors which influence HBsAg loss. It may be possible to develop a nomogram which intercalates these factors; however, further research should consider immune processes involved in HBsAg loss.
Keywords: HBsAg; MMP-1; TNF-R1; chemokine; interferon.
Copyright © 2022 Yuan, Fu, Xiao, He, Ji, Seery, Zhang, Ye, Zhou, Kong, Zhang, Zhou, Lin, Jia, Liang, Tang, Wang, Zhang and Shao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson R, Choi H, Lenz O, Peters M, Janssen H, Mishra P, et al. Association between seroclearance of hepatitis b surface antigen and long-term clinical outcomes of patients with chronic hepatitis b virus infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol (2021) 19:463–72. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.05.041 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

