Infection with the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in children with congenital heart disease: A case series study during Shanghai epidemic
- PMID: 36304543
- PMCID: PMC9592748
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1001780
Infection with the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in children with congenital heart disease: A case series study during Shanghai epidemic
Abstract
Objective: To analyze the clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron variant infections in children with congenital heart disease (CHD).
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed on SARS-CoV-2 Omicron-infected children with CHD who were admitted to Shanghai Children's Medical Center from April 1, 2022 to May 31, 2022. The clinical, laboratory and imaging data, and the nucleic acid conversion time of the children in this group were collected and analyzed.
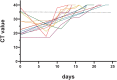
Results: Thirteen patients were included in this study and had an average age of 1.1 (0.16-14) years. Among the patients, 3 patients were preoperatively treated, and 10 were postoperatively treated. According to the severity of the disease, 1 patient was diagnosed with the moderate type, and the remaining 12 patients were diagnosed with the mild type. The clinical symptoms were mostly associated with upper respiratory tract infections, including 13 with fever (100%), 8 with cough (61.8%), 5 with sputum production (38.5%), 1 of shortness of breath (7.7%), etc. All patients were successfully discharged from the hospital, with 16.4 ± 2.9 days needed to obtain cycle threshold (CT) values ≥35 in nucleic acid testing and 17.5 ± 3.6 days of hospitalization.
Conclusions: For vulnerable patients such as children with CHD, SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infections mostly present with mild upper respiratory tract symptoms with negative or mildly changed chest imaging. Through appropriate treatment of the underlying disease in the quarantine ward, patients might obtain good outcomes, even after long periods of hospitalization.
Keywords: Omicron; children; congenital heart disease; coronavirus; infectious disease.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Wu, Zhang, Cao, Zhang, Zhang and Dong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2022). Available online at: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on.... (accessed June 26, 2022).
-
- WHO . Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern. (2021). Available online at: https://www.who.int/news/item/26-11-2021-classification-of-omicron-(b.1.... (accessed June 26, 2022).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous