Heart failure and cancer: From active exposure to passive adaption
- PMID: 36304546
- PMCID: PMC9592839
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.992011
Heart failure and cancer: From active exposure to passive adaption
Abstract
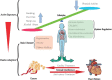
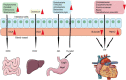
The human body seems like a "balance integrator." On the one hand, the body constantly actively receives various outside stimuli and signals to induce changes. On the other hand, several internal regulations would be initiated to adapt to these changes. In most cases, the body could keep the balance in vitro and in vivo to reach a healthy body. However, in some cases, the body can only get to a pathological balance. Actively exposed to unhealthy lifestyles and passively adapting to individual primary diseases lead to a similarly inner environment for both heart failure and cancer. To cope with these stimuli, the body must activate the system regulation mechanism and face the mutual interference. This review summarized the association between heart failure and cancer from active exposure to passive adaption. Moreover, we hope to inspire researchers to contemplate these two diseases from the angle of overall body consideration.
Keywords: Cardio-Oncology; active exposure; cancer; heart failure; passive adaption.
Copyright © 2022 Du and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

