Acute effects of combined isometric and plyometric conditioning activities on sports performance and tendon stiffness in female volleyball players
- PMID: 36304585
- PMCID: PMC9593028
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1025839
Acute effects of combined isometric and plyometric conditioning activities on sports performance and tendon stiffness in female volleyball players
Abstract
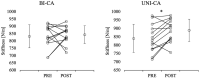
This study aimed to compare the effects of bilateral and unilateral conditioning activities (CA; combined isometric and plyometric) on countermovement jump performance, modified t-agility test, Achilles tendon stiffness and skin surface temperature. Thirteen female semi-professional volleyball players performed two CAs in random order: 1) bilateral isometric half back squats followed by bilateral drop jumps (BI-CA); and 2) unilateral isometric half back squats followed by unilateral drop jumps (UNI-CA). To assess the effects of CAs, countermovement jump, modified t-agility test, Achilles tendon stiffness and skin surface temperature measurements were performed 5 min before and 6 min after the CA. Both CAs significantly increased thigh skin surface temperature from pre- to post-CA (BI-CA, p < 0.001; effect size [ES] = 1.41 and UNI-CA, p = 0.001; ES = 1.39) but none of them influenced modified t-agility test time (interaction: p = 0.338, main effect of time: p = 0.121 and condition: p = 0.819). The countermovement jump height and modified reactive strength index significantly increased from pre-to post-CA during the BI-CA condition (p = 0.003, ES = 0.45, and p = 0.008, ES = 0.48) but not for UNI-CA (p = 0.061, ES = 0.18 and p = 0.065, ES = 0.26). No significant impact has been found for countermovement depth (interaction: p = 0.054, main effect of time: 0.097, and condition: p = 0.41) as well as for contraction time (interaction: p = 0.536, main effect of time: p = 0.224, and condition: p = 0.807). Moreover, stronger and weaker limb CMJ relative peak force significantly decreased from pre-to post-CA (p = 0.014, ES = -0.31, and p = 0.027, ES = -0.26; respectively) during UNI-CA condition but not for BI-CA (p = 0.096, ES = 0.23, and p = 1.41, ES = 0.18). The stronger and weaker limb Achilles tendon stiffness significantly increased from pre-to post-CA during the UNI-CA condition (p = 0.013, ES = 0.60 and p < 0.001, ES = 0.79; respectively) but not for BI-CA (p = 0.66; ES = 0.15 and p = 0.265; ES = 0.42). Furthermore, the post-CA stronger limb Achilles tendon stiffness during the UNI-CA was significantly higher than that noted during the BI-CA (p = 0.006, ES = 0.7). The present study showed that combined isometric and plyometric bilateral CA effectively improved the countermovement jump but did not enhance the t-agility test performance. These findings indicate that exercise combinations could effectively produce a post-activation performance enhancement effect but should replicate the following explosive task as much as possible.
Keywords: athletic performance; change of direction; countermovement jump (CMJ); myotonometry; post-activation performance enhancement; post-activation potentiation; resistance training; skin surface temperature.
Copyright © 2022 Kalinowski, Pisz, Kolinger, Wilk, Stastny and Krzysztofik.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Alenezi F., Herrington L., Jones P., Jones R. (2014). Relationships between lower limb biomechanics during single leg squat with running and cutting tasks: A preliminary investigation. Br. J. Sports Med. 48, 560.3–561. 10.1136/bjsports-2014-093494.3 - DOI
-
- Bishop C., Turner A., Jordan M., Harry J., Loturco I., Lake J., et al. (2022). A framework to guide practitioners for selecting metrics during the countermovement and drop jump tests. Strength Cond. J. 44, 95–103. 10.1519/SSC.0000000000000677 - DOI
-
- Campbell M. J., Walters S. J. K., Machin D. (2021). Medical statistics: A textbook for the health sciences. Fifth Edition. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley Blackwell.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

