Pretreatment Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Lactate Dehydrogenase Predict the Prognosis of Metastatic Cervical Cancer Treated with Combination Immunotherapy
- PMID: 36304986
- PMCID: PMC9596258
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1828473
Pretreatment Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Lactate Dehydrogenase Predict the Prognosis of Metastatic Cervical Cancer Treated with Combination Immunotherapy
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors have considerably changed the treatment paradigm for metastatic cervical cancer; nonetheless, only a proportion of patients achieve a durable response. Therefore, exploring the predictive biomarkers of immunotherapy response is of crucial importance. This study aimed to evaluate the predictive and prognostic value of hematological parameters in patients with metastatic cervical cancer treated with combination immunotherapy.
Methods: Clinical data of patients with metastatic cervical cancer treated with combination immunotherapy between June 2019 and April 2021 were retrospectively analyzed. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was performed to determine the cut-off values of continuous variables, and binary logistic analysis was conducted to compare the treatment response between groups. The Kaplan-Meier method was applied for survival analysis. A Cox proportional hazards regression model was used to identify factors associated with progression-free survival (PFS).
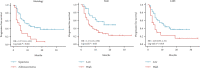
Results: Seventy patients were included in this study. The cut-off values for the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) were 5.33 and 195.00 U/L, respectively. High pretreatment NLR (≥5.33) was correlated with decreased objective response rate (53.19% vs. 78.26%, p = 0.048). The survival analysis revealed that high pretreatment NLR (hazard ratio [HR] = 2.401, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.151-5.009, p = 0.020) and LDH level (HR = 1.987, 95% CI: 1.029-3.835, p = 0.041) were independent prognostic factors associated with short PFS.
Conclusions: Our study suggested that high pretreatment NLR and LDH values were independently correlated with poor survival in patients with metastatic cervical cancer treated with combination immunotherapy. Pretreatment NLR and LDH values could serve as potential biomarkers that may aid in the selection of patients who would benefit from combination immunotherapy. Further prospective studies investigating the prognostic value of NLR and LDH are warranted. Trial registration number: UHCT22008.
Copyright © 2022 Mingxia Cheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Naumann R. W., Hollebecque A., Meyer T., et al. Safety and efficacy of nivolumab monotherapy in recurrent or metastatic cervical, vaginal, or vulvar carcinoma: results from the phase I/II CheckMate 358 trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology . 2019;37(31):2825–2834. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00739. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous