Instrumented difference-in-differences
- PMID: 36305081
- PMCID: PMC10484497
- DOI: 10.1111/biom.13783
Instrumented difference-in-differences
Abstract
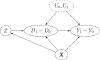
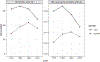
Unmeasured confounding is a key threat to reliable causal inference based on observational studies. Motivated from two powerful natural experiment devices, the instrumental variables and difference-in-differences, we propose a new method called instrumented difference-in-differences that explicitly leverages exogenous randomness in an exposure trend to estimate the average and conditional average treatment effect in the presence of unmeasured confounding. We develop the identification assumptions using the potential outcomes framework. We propose a Wald estimator and a class of multiply robust and efficient semiparametric estimators, with provable consistency and asymptotic normality. In addition, we extend the instrumented difference-in-differences to a two-sample design to facilitate investigations of delayed treatment effect and provide a measure of weak identification. We demonstrate our results in simulated and real datasets.
Keywords: causal inference; effect modification; exclusion restriction; instrumental variables; multiple robustness.
© 2022 The International Biometric Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Discussion on "Instrumented difference-in-differences" by Ting Ye, Ashkan Ertefaie, James Flory, Sean Hennessy & Dylan S. Small.Biometrics. 2023 Jun;79(2):592-596. doi: 10.1111/biom.13784. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Biometrics. 2023. PMID: 36346088
-
Discussion on "Instrumented difference-in-differences" by Ting Ye, Ashkan Ertefaie, James Flory, Sean Hennessy, and Dylan S. Small.Biometrics. 2023 Jun;79(2):582-586. doi: 10.1111/biom.13779. Epub 2022 Nov 11. Biometrics. 2023. PMID: 36369777
-
Discussion on: Instrumented difference-in-differences, by Ting Ye, Ashkan Ertefaie, James Flory, Sean Hennessy and Dylan S. Small.Biometrics. 2023 Jun;79(2):597-600. doi: 10.1111/biom.13785. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Biometrics. 2023. PMID: 36408762
-
Discussion on "Instrumented difference-in-differences" by Ye, Ertefaie, Flory, Hennessy, Small.Biometrics. 2023 Jun;79(2):587-591. doi: 10.1111/biom.13781. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Biometrics. 2023. PMID: 36448885
References
-
- Abadie A (2003) Semiparametric instrumental variable estimation of treatment response models. Journal of Econometrics, 113, 231–263.
-
- Abadie A (2005) Semiparametric difference-in-differences estimators. The Review of Economic Studies, 72, 1–19.
-
- Angrist JD, Imbens GW & Rubin DB (1996) Identification of causal effects using instrumental variables. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 91, 444–455.
-
- Angrist JD & Krueger AB (1992) The effect of age at school entry on educational attainment: an application of instrumental variables with moments from two samples. Journal of the American statistical Association, 87, 328–336.
-
- Angrist JD & Krueger AB (1995) Split-sample instrumental variables estimates of the return to schooling. Journal of Business & Economic Statistics, 13, 225–235.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

