Discovery of host-directed modulators of virus infection by probing the SARS-CoV-2-host protein-protein interaction network
- PMID: 36305426
- PMCID: PMC9677461
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbac456
Discovery of host-directed modulators of virus infection by probing the SARS-CoV-2-host protein-protein interaction network
Abstract
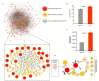
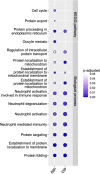
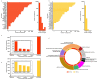
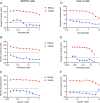
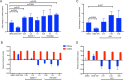
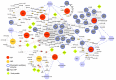
The ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has highlighted the need to better understand virus-host interactions. We developed a network-based method that expands the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2)-host protein interaction network and identifies host targets that modulate viral infection. To disrupt the SARS-CoV-2 interactome, we systematically probed for potent compounds that selectively target the identified host proteins with high expression in cells relevant to COVID-19. We experimentally tested seven chemical inhibitors of the identified host proteins for modulation of SARS-CoV-2 infection in human cells that express ACE2 and TMPRSS2. Inhibition of the epigenetic regulators bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) and histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2), along with ubiquitin-specific peptidase (USP10), enhanced SARS-CoV-2 infection. Such proviral effect was observed upon treatment with compounds JQ1, vorinostat, romidepsin and spautin-1, when measured by cytopathic effect and validated by viral RNA assays, suggesting that the host proteins HDAC2, BRD4 and USP10 have antiviral functions. We observed marked differences in antiviral effects across cell lines, which may have consequences for identification of selective modulators of viral infection or potential antiviral therapeutics. While network-based approaches enable systematic identification of host targets and selective compounds that may modulate the SARS-CoV-2 interactome, further developments are warranted to increase their accuracy and cell-context specificity.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; cell context specificity; host modulators; network prioritization; protein–protein interactions.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Kinome-Wide Small Interfering RNA Screen Identifies Proviral and Antiviral Host Factors in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Replication, Including Double-Stranded RNA-Activated Protein Kinase and Early Secretory Pathway Proteins.J Virol. 2015 Aug;89(16):8318-33. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01029-15. Epub 2015 Jun 3. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26041291 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the SARS-CoV-2-Host Protein-Protein Interactome by Affinity Purification Mass Spectrometry and Proximity-Dependent Biotin Labeling: A Rational and Straightforward Route to Discover Host-Directed Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutics.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 7;22(2):532. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020532. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33430309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery and Evaluation of Entry Inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 and Its Emerging Variants.J Virol. 2021 Nov 23;95(24):e0143721. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01437-21. Epub 2021 Sep 22. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34550770 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of HDAC2 with SARS-CoV-2 NSP5 and IRF3 Is Not Required for NSP5-Mediated Inhibition of Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0232222. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02322-22. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36173315 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus Infection-Associated Cell Death Signaling and Potential Therapeutic Targets.Molecules. 2021 Dec 9;26(24):7459. doi: 10.3390/molecules26247459. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34946543 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of histone deacetylase inhibitors in non-neoplastic diseases.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 2;10(13):e33997. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33997. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39071622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proximity interactome of alphavirus replicase component nsP3 includes proviral host factors eIF4G and AHNAK.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Apr 7;21(4):e1013050. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013050. eCollection 2025 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40193402 Free PMC article.
-
Role of E3 ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinating enzymes in SARS-CoV-2 infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Jun 9;13:1217383. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1217383. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37360529 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

