Tissue-resident immunity in the lung: a first-line defense at the environmental interface
- PMID: 36305904
- PMCID: PMC9614767
- DOI: 10.1007/s00281-022-00964-2
Tissue-resident immunity in the lung: a first-line defense at the environmental interface
Abstract
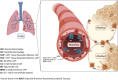
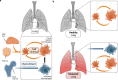
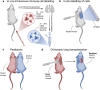
The lung is a vital organ that incessantly faces external environmental challenges. Its homeostasis and unimpeded vital function are ensured by the respiratory epithelium working hand in hand with an intricate fine-tuned tissue-resident immune cell network. Lung tissue-resident immune cells span across the innate and adaptive immunity and protect from infectious agents but can also prove to be pathogenic if dysregulated. Here, we review the innate and adaptive immune cell subtypes comprising lung-resident immunity and discuss their ontogeny and role in distinct respiratory diseases. An improved understanding of the role of lung-resident immunity and how its function is dysregulated under pathological conditions can shed light on the pathogenesis of respiratory diseases.
Keywords: Asthma; Cancer; Infections; Lung; Metastasis; Tissue-resident immunity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tissue-resident innate immunity in the lung.Immunology. 2020 Mar;159(3):245-256. doi: 10.1111/imm.13143. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Immunology. 2020. PMID: 31670391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multilayered Immunity by Tissue-Resident Lymphocytes in Cancer.Annu Rev Immunol. 2024 Jun;42(1):647-677. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-083122-043836. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Annu Rev Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38424658 Review.
-
Lung-resident lymphocytes and their roles in respiratory infections and chronic respiratory diseases.Chin Med J Pulm Crit Care Med. 2024 Dec 18;2(4):214-223. doi: 10.1016/j.pccm.2024.11.006. eCollection 2024 Dec. Chin Med J Pulm Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 39834580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Guards at the gate: physiological and pathological roles of tissue-resident innate lymphoid cells in the lung.Protein Cell. 2017 Dec;8(12):878-895. doi: 10.1007/s13238-017-0379-5. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Protein Cell. 2017. PMID: 28271447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate immune memory of tissue-resident macrophages and trained innate immunity: Re-vamping vaccine concept and strategies.J Leukoc Biol. 2020 Sep;108(3):825-834. doi: 10.1002/JLB.4MR0220-446R. Epub 2020 Mar 3. J Leukoc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32125045 Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk between circadian clocks and pathogen niche.PLoS Pathog. 2024 May 9;20(5):e1012157. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012157. eCollection 2024 May. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38723104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-17A-Induced Redox Imbalance and Inflammatory Responses in Mice Lung via Act1-TRAF6-IKBα Signaling Pathway: Implications for Lung Disease Pathogenesis.Inflammation. 2025 Aug;48(4):2417-2430. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02199-9. Epub 2024 Nov 28. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 39607627
-
Towards early detection and disease interception of COPD across the lifespan.Eur Respir Rev. 2025 Jul 9;34(177):240243. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0243-2024. Print 2025 Jul. Eur Respir Rev. 2025. PMID: 40633975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Occupationally Relevant Zinc- and Copper-Containing Metal Fumes Inhibit Human THP-1 Macrophage TNF and IL-6 Responses to Bacterial Stimuli.Glob Chall. 2024 Dec 31;9(5):2400302. doi: 10.1002/gch2.202400302. eCollection 2025 May. Glob Chall. 2024. PMID: 40352634 Free PMC article.
-
Nonclinical strategies and considerations to enable the redosing of gene therapies.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2025 Jun 25;33(3):101520. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2025.101520. eCollection 2025 Sep 11. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2025. PMID: 40687375 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

