Multi-omic analyses of changes in the tumor microenvironment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma following neoadjuvant treatment with anti-PD-1 therapy
- PMID: 36306792
- PMCID: PMC9669212
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.10.001
Multi-omic analyses of changes in the tumor microenvironment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma following neoadjuvant treatment with anti-PD-1 therapy
Abstract
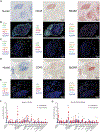
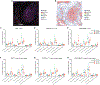
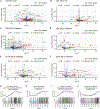
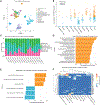
Successful pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) immunotherapy necessitates optimization and maintenance of activated effector T cells (Teff). We prospectively collected and applied multi-omic analyses to paired pre- and post-treatment PDAC specimens collected in a platform neoadjuvant study of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-secreting allogeneic PDAC vaccine (GVAX) vaccine ± nivolumab (anti-programmed cell death protein 1 [PD-1]) to uncover sensitivity and resistance mechanisms. We show that GVAX-induced tertiary lymphoid aggregates become immune-regulatory sites in response to GVAX + nivolumab. Higher densities of tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs) following GVAX + nivolumab portend poorer overall survival (OS). Increased T cells expressing CD137 associated with cytotoxic Teff signatures and correlated with increased OS. Bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing found that nivolumab alters CD4+ T cell chemotaxis signaling in association with CD11b+ neutrophil degranulation, and CD8+ T cell expression of CD137 was required for optimal T cell activation. These findings provide insights into PD-1-regulated immune pathways in PDAC that should inform more effective therapeutic combinations that include TAN regulators and T cell activators.
Keywords: CD137; IL-8; RNA sequencing; Th17; anti-PD-1 antibody; immune checkpoint inhibitor; multiplex immunohistochemistry; pancreatic cancer; tumor-associated neutrophils; vaccine therapy.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests L.Z. receives grant support from Bristol-Meyer Squibb, Merck, AstraZeneca, iTeos, Amgen, NovaRock, Inxmed, Halozyme, and Abmeta. L.Z. is a paid consultant/Advisory Board member at Biosion, Alphamab, NovaRock, Ambrx, Akrevia/Xilio, QED, Natera, Novagenesis, Snow Lake Capitals, BioArdis, Tempus, Amberstone, Pfizer, Tavotek, and Mingruizhiyao. L.Z. holds shares at Alphamab, Amberstone, and Mingruizhiyao. E.J.F. is on the scientific advisory board of Resistance Bio and is a paid consultant for Merck and Mestag Therapeutics. E.J. receives grant support from Lustgarten Foundation, Bristol-Meyer Squibb, Genentech, and AstroZeneca; is a paid consultant for NextCure, Genocea, DragonFly, Stimit, CSTONE, Achilles, and Candel; is on the advisory board of Parker Institute and Break Through Cancer; is a founder of Abmeta Biotech; and is the Chief Medical Advisor for the Lustgarten Foundation.
Figures



References
-
- Avram G, Sánchez-Sendra B, Martín JM, Terrádez L, Ramos D, and Monteagudo C (2013). The density and type of MECA-79-positive high endothelial venules correlate with lymphocytic infiltration and tumour regression in primary cutaneous melanoma. Histopathology 63, 852–861. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

