Transcriptome analysis of mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves to identify differentially expressed genes associated with post-harvest shelf-life elongation
- PMID: 36307466
- PMCID: PMC9616847
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-21828-7
Transcriptome analysis of mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves to identify differentially expressed genes associated with post-harvest shelf-life elongation
Abstract
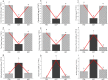
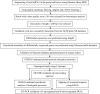
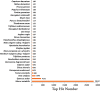
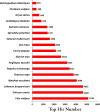
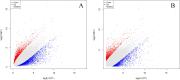
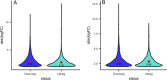
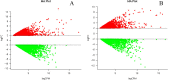
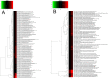
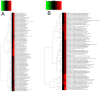
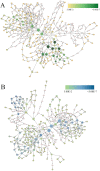
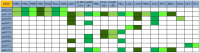
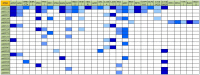
Present study deals with molecular expression patterns responsible for post-harvest shelf-life extension of mulberry leaves. Quantitative profiling showed retention of primary metabolite and accumulation of stress markers in NS7 and CO7 respectively. The leaf mRNA profiles was sequenced using the Illumina platform to identify DEGs. A total of 3413 DEGs were identified between the treatments. Annotation with Arabidopsis database has identified 1022 DEGs unigenes. STRING generated protein-protein interaction, identified 1013 DEGs nodes with p < 1.0e-16. KEGG classifier has identified genes and their participating biological processes. MCODE and BiNGO detected sub-networking and ontological enrichment, respectively at p ≤ 0.05. Genes associated with chloroplast architecture, photosynthesis, detoxifying ROS and RCS, and innate-immune response were significantly up-regulated, responsible for extending shelf-life in NS7. Loss of storage sucrose, enhanced activity of senescence-related hormones, accumulation of xenobiotics, and development of osmotic stress inside tissue system was the probable reason for tissue deterioration in CO7. qPCR validation of DEGs was in good agreement with RNA sequencing results, indicating the reliability of the sequencing platform. Present outcome provides a molecular insight regarding involvement of genes in self-life extension, which might help the sericulture industry to overcome their pre-existing problems related to landless farmers and larval feeding during monsoon.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Genome-wide transcriptome profiling of mulberry (Morus alba) response to boron deficiency and toxicity reveal candidate genes associated with boron tolerance in leaves.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024 Feb;207:108316. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.108316. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38176189
-
Molecular mechanism of mulberry response to drought stress revealed by complementary transcriptomic and iTRAQ analyses.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Jan 17;22(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03410-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35039015 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and Verification of Photosynthesis and Chloroplast-Related Genes in Mulberry by Comparative RNA-Seq and Virus-Induced Gene Silencing.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 3;23(15):8620. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158620. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955752 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Identifies Key Defense Genes and Mechanisms in Mulberry (Morus alba) Leaves against Silkworms (Bombyx mori).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 4;23(21):13519. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113519. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362309 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of starch and sucrose metabolism across bulb development in Sagittaria sagittifolia.Gene. 2018 Apr 5;649:99-112. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.01.075. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29374598 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Genes Associated with Flooding Tolerance in Mulberry Plants.Life (Basel). 2023 Apr 26;13(5):1087. doi: 10.3390/life13051087. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37240733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rahmathulla VK. Management of climatic factors for successful silkworm (Bombyx mori L.) crop and higher silk production: A Review. Psyche. 2012 doi: 10.1155/2012/121234. - DOI
-
- Bukhari R, Kour H. Background, current scenario and future challenges of the indian silk industry. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2019;8(5):2448–2463.
-
- Lakshmanan S, Balasaraswathi S, Mani A. Rural labour employment through mulberry sericulture: An analysis of cross sectional study. J. Rural Dev. 2011;30(2):155–167.
-
- Kumaresan, P., Jaishankar, Qadri, S.M.H. Impact of urbanisation on sericulture development in Karnataka. J. Rural Dev. (Hyderabad) 29(2), 113–123 (2010).
-
- Sharma P, Jha AB, Dubey RS, Pessarakli M. Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage, and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. J. Bot. 2012 doi: 10.1155/2012/217037. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

