Towards the engineering of a photon-only two-stroke rotary molecular motor
- PMID: 36307476
- PMCID: PMC9616945
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-33695-x
Towards the engineering of a photon-only two-stroke rotary molecular motor
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Towards the engineering of a photon-only two-stroke rotary molecular motor.Nat Commun. 2022 Dec 7;13(1):7541. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35006-w. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36476995 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
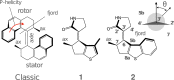
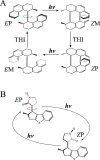
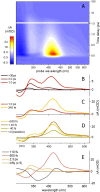
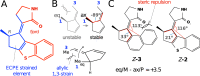
The rational engineering of photoresponsive materials, e.g., light-driven molecular motors, is a challenging task. Here, we use structure-related design rules to prepare a prototype molecular rotary motor capable of completing an entire revolution using, exclusively, the sequential absorption of two photons; i.e., a photon-only two-stroke motor. The mechanism of rotation is then characterised using a combination of non-adiabatic dynamics simulations and transient absorption spectroscopy measurements. The results show that the rotor moiety rotates axially relative to the stator and produces, within a few picoseconds at ambient T, an intermediate with the same helicity as the starting structure. We discuss how such properties, that include a 0.25 quantum efficiency, can help overcome the operational limitations of the classical overcrowded alkene designs.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Browne W, Feringa BL. Making molecular machines work. Nat. Nanotech. 2006;1:25–35. - PubMed
-
- Balzani V, Credi A, Venturi M. Light powered molecular machines. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009;38:1542–1550. - PubMed
-
- Feringa BL. The art of building small: from molecular switches to motors (nobel lecture) Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017;56:11060–11078. - PubMed
-
- Kassem S, et al. Artificial molecular motors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017;46:2592–2621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

