Real-time COVID-19 detection via graphite oxide-based field-effect transistor biosensors decorated with Pt/Pd nanoparticles
- PMID: 36307495
- PMCID: PMC9614753
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-22249-2
Real-time COVID-19 detection via graphite oxide-based field-effect transistor biosensors decorated with Pt/Pd nanoparticles
Abstract
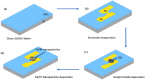
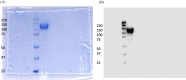
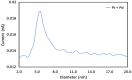
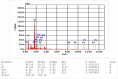
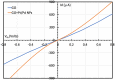
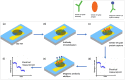
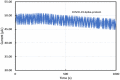
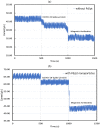
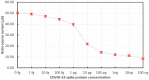
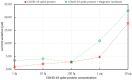
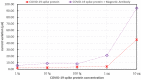
Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) spreads an extremely infectious disease where there is no specific treatment. COVID-19 virus had a rapid and unexpected spread rate which resulted in critical difficulties for public health and unprecedented daily life disruption. Thus, accurate, rapid, and early diagnosis of COVID-19 virus is critical to maintain public health safety. A graphite oxide-based field-effect transistor (GO-FET) was fabricated and functionalized with COVID-19 antibody for the purpose of real-time detection of COVID-19 spike protein antigen. Thermal evaporation process was used to deposit the gold electrodes on the surface of the sensor substrate. Graphite oxide channel was placed between the gold electrodes. Bimetallic nanoparticles of platinum and palladium were generated via an ultra-high vacuum (UHV) compatible system by sputtering and inert-gas condensation technique. The biosensor graphite oxide channel was immobilized with specific antibodies against the COVID-19 spike protein to achieve selectivity and specificity. This technique uses the attractive semiconductor characteristics of the graphite oxide-based materials resulting in highly specific and sensitive detection of COVID-19 spike protein. The GO-FET biosensor was decorated with bimetallic nanoparticles of platinum and palladium to investigate the improvement in the sensor sensitivity. The in-house developed biosensor limit of detection (LOD) is 1 fg/mL of COVID-19 spike antigen in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Moreover, magnetic labelled SARS-CoV-2 spike antibody were studied to investigate any enhancement in the sensor performance. The results indicate the successful fabrication of a promising field effect transistor biosensor for COVID-19 diagnosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

