Polygenic Health Index, General Health, and Pleiotropy: Sibling Analysis and Disease Risk Reduction
- PMID: 36307513
- PMCID: PMC9616929
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-22637-8
Polygenic Health Index, General Health, and Pleiotropy: Sibling Analysis and Disease Risk Reduction
Abstract
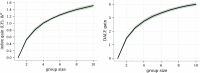
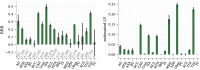
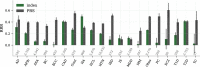
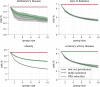
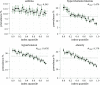
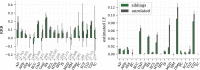
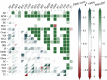
We construct a polygenic health index as a weighted sum of polygenic risk scores for 20 major disease conditions, including, e.g., coronary artery disease, type 1 and 2 diabetes, schizophrenia, etc. Individual weights are determined by population-level estimates of impact on life expectancy. We validate this index in odds ratios and selection experiments using unrelated individuals and siblings (pairs and trios) from the UK Biobank. Individuals with higher index scores have decreased disease risk across almost all 20 diseases (no significant risk increases), and longer calculated life expectancy. When estimated Disability Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) are used as the performance metric, the gain from selection among ten individuals (highest index score vs average) is found to be roughly 4 DALYs. We find no statistical evidence for antagonistic trade-offs in risk reduction across these diseases. Correlations between genetic disease risks are found to be mostly positive and generally mild. These results have important implications for public health and also for fundamental issues such as pleiotropy and genetic architecture of human disease conditions.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing interests: SH is a founder, shareholder, and serves on the Board of Directors of Genomic Prediction, Inc. (GP). LT is a founder, shareholder, serves on the Board of Directors, and is the CEO of GP. EW and LL are employees and shareholders of GP. TR declares no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Wray, N. R. et al. From basic science to clinical application of polygenic risk scores: A primer. JAMA Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.3049 (2020) - PubMed
-
- Torkamani A, Wineinger NE, Topol EJ. The personal and clinical utility of polygenic risk scores. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018;19:581. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

