The reliability of the measurement of muscle volume using magnetic resonance imaging in typically developing infants by two raters
- PMID: 36307532
- PMCID: PMC9616850
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-23087-y
The reliability of the measurement of muscle volume using magnetic resonance imaging in typically developing infants by two raters
Abstract
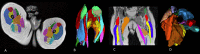
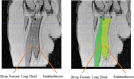
To assess intra-rater and inter-rater reliability of the manual segmentation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) for the in vivo measurement of infant muscle volume of the knee extensor and flexor muscles by two raters. Muscles of the knee extensor and flexor muscle of ten typically developing infants (86 days ± 7 days) were scanned with MRI (Proton density sequence). Scans were then segmented using Slicer software, and volumes rendered by two raters. Intra-rater and inter-rater reliability were assessed using intra-class correlation (ICC), with mean difference (MD), standard error of the mean (SEM), and minimal detectable change (MDC) for each muscle calculated. ICCs for Intra-rater reliability of the segmentation process for the muscle volume of the muscles of the knee extensors and flexor muscles were 0.901-0.972, and 0.776-0.945 respectively, with inter-rater reliabilities between 0.914-0.954 and 0.848-0.978, for the knee extensor and flexors muscles respectively. For intra-rater reliability, MD ≤ - 0.47 cm3, MDCs for were < 1.09 cm3 and for inter-rater MD ≤ - 1.40 cm3, MDCs for were < 1.63 cm3 for all muscles. MRI segmentation for muscle volumes showed good to excellent reliability, though given the small volumes of the muscles themselves, variations between raters are amplified. Care should be taken in the reporting and interpretation of infant muscle volume.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Validity and reliability of a freehand 3D ultrasound system for the determination of triceps surae muscle volume in children with cerebral palsy.J Anat. 2019 Mar;234(3):384-391. doi: 10.1111/joa.12927. Epub 2018 Dec 7. J Anat. 2019. PMID: 30525186 Free PMC article.
-
The reliability and validity of triceps surae muscle volume assessment using freehand three-dimensional ultrasound in typically developing infants.J Anat. 2022 Mar;240(3):567-578. doi: 10.1111/joa.13565. Epub 2021 Oct 24. J Anat. 2022. PMID: 34693531 Free PMC article.
-
Intra- and inter-rater reliability, agreement, and minimal detectable change of the handheld dynamometer in individuals with symptomatic hip osteoarthritis.PLoS One. 2023 Jun 8;18(6):e0278086. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278086. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37289803 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-rater and Inter-rater Reliability of the KangaTech (KT360) Fixed Frame Dynamometry System During Maximal Isometric Strength Measurements of the Knee Flexors.Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2024 Nov 2;19(11):1397-1406. doi: 10.26603/001c.124121. eCollection 2024. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2024. PMID: 39502541 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying skeletal muscle volume and shape in humans using MRI: A systematic review of validity and reliability.PLoS One. 2018 Nov 29;13(11):e0207847. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207847. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30496308 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Updates on Methods for Body Composition Analysis: Implications for Clinical Practice.Curr Obes Rep. 2025 Jan 11;14(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s13679-024-00593-w. Curr Obes Rep. 2025. PMID: 39798028 Review.
-
Which muscle is the external rotation compensator after superior capsular reconstruction?JSES Int. 2024 Sep 27;9(1):123-129. doi: 10.1016/j.jseint.2024.09.010. eCollection 2025 Jan. JSES Int. 2024. PMID: 39898197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klitgaard H, Mantoni M, Schiaffino S, Ausoni S, Gorza L, Laurent-Winter C, et al. Function, morphology and protein expression of ageing skeletal muscle: A cross-sectional study of elderly men with different training backgrounds. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1990;140(1):41–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1990.tb08974.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

