PDE12 in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 36307540
- PMCID: PMC9614732
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-22890-x
PDE12 in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
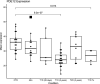
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) incidence is increased after COVID-19 infection in children under 18 years of age. Interferon-α-activated oligoadenylate synthetase and downstream RNAseL activation degrade pathogen RNA, but can also damage host RNA when RNAseL activity is poorly regulated. One such regulator is PDE12 which degrades 2'-5' oligoadenylate units, thereby decreasing RNAseL activity. We analyzed PDE12 expression in islets from non-diabetic donors, individuals with newly (median disease duration 35 days) and recently (5 years) diagnosed T1D, and individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D). We also analyzed PDE12 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) relative to T1D incidence. PDE12 expression was decreased in individuals with recently diagnosed T1D, in three of five individuals with newly diagnosed T1D, but not in individuals with T2D. Two rare PDE12 SNPs were found to have odds ratios of 1.80 and 1.74 for T1D development. We discuss whether decreased PDE12 expression after COVID-19 infection might be part of the up to 2.5-fold increase in T1D incidence.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of phosphodiesterase 12 results in antiviral activity against several RNA viruses including SARS-CoV-2.J Gen Virol. 2023 Jul;104(7). doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001865. J Gen Virol. 2023. PMID: 37432877
-
Expression-based Genome-wide Association Study Links OPN and IL1-RA With Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes in Children.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Jun 16;107(7):1825-1832. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac256. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 35460250 Free PMC article.
-
Increase in the Diagnosis and Severity of Presentation of Pediatric Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes during the COVID-19 Pandemic.Horm Res Paediatr. 2021;94(7-8):275-284. doi: 10.1159/000519797. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Horm Res Paediatr. 2021. PMID: 34564073 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence, incidence and mortality of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in Denmark 1996-2016.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020 May;8(1):e001071. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2019-001071. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020. PMID: 32475839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monogenic Diabetes: What It Teaches Us on the Common Forms of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes.Endocr Rev. 2016 Jun;37(3):190-222. doi: 10.1210/er.2015-1116. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Endocr Rev. 2016. PMID: 27035557 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endocrinological Involvement in Children and Adolescents Affected by COVID-19: A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Aug 11;12(16):5248. doi: 10.3390/jcm12165248. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37629291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beta-cell activity and development of Type 1 diabetes.APMIS. 2025 Jan;133(1):e13441. doi: 10.1111/apm.13441. Epub 2024 May 26. APMIS. 2025. PMID: 38798081 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

