18β-Glycyrrhetinic Acid Ameliorates Neuroinflammation Linked Depressive Behavior Instigated by Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress via Triggering BDNF/TrkB Signaling Pathway in Rats
- PMID: 36307572
- PMCID: PMC9616426
- DOI: 10.1007/s11064-022-03779-7
18β-Glycyrrhetinic Acid Ameliorates Neuroinflammation Linked Depressive Behavior Instigated by Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress via Triggering BDNF/TrkB Signaling Pathway in Rats
Abstract
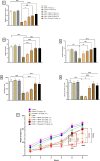
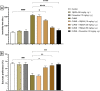
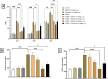
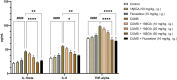
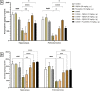
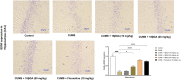
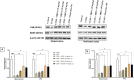
Evidence shows that inflammatory responses may encompass the onset of severe depressive illness. Traditionally used licorice contains 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid (18βGA), which has been demonstrated to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress. This study investigates the antidepressant effects of 18βGA and the underlying mechanism in rats exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS). Wistar rats were exposed to CUMS for 36 consecutive days to establish depression. 18βGA (10, 20, and 50 mg/kg) or fluoxetine was given once daily (from day 30 to day 36). Thereafter, behavior parameters (sucrose preference test, forced-swimming test, open-field test, body weight), pro-inflammatory cytokines, neurotransmitters, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), corticosterone (CORT), and liver biomarkers were studied. Immunohistochemistry and western blot analyses were conducted to investigate the protein's expression. 18βGA (20 and 50 mg/kg) treatment increased sucrose intake, locomotion in the open-field test, decreased immobility time in the forced swim test, and improved body weight in CUMS-exposed rats. The therapy of 18βGA dramatically declined cytokines, ACTH and CORT and improved 5HT and norepinephrine in CUMS rats. Furthermore, BDNF and TrkB proteins were down-regulated in CUMS group, which was increased to varying degrees by 18βGA at doses of 20 and 50 mg/kg. Therefore, 18βGA ameliorates depressive-like behavior persuaded by chronic unpredictable mild stress, decreases neuroinflammation, liver biomarkers, stress hormones, and improves body weight, brain neurotransmitter concentration via activating on BDNF/TrkB signaling pathway in both PFC and hippocampus in rats.
Keywords: 18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid; Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Chronic unpredictable mild stress; Depression; Tropomyosin receptor kinase B.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

