Wasteosomes (corpora amylacea) of human brain can be phagocytosed and digested by macrophages
- PMID: 36307854
- PMCID: PMC9617366
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-022-00915-2
Wasteosomes (corpora amylacea) of human brain can be phagocytosed and digested by macrophages
Abstract
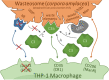
Background: Corpora amylacea of human brain, recently renamed as wasteosomes, are granular structures that appear during aging and also accumulate in specific areas of the brain in neurodegenerative conditions. Acting as waste containers, wasteosomes are formed by polyglucosan aggregates that entrap and isolate toxic and waste substances of different origins. They are expelled from the brain to the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and can be phagocytosed by macrophages. In the present study, we analyze the phagocytosis of wasteosomes and the mechanisms involved in this process. Accordingly, we purified wasteosomes from post-mortem extracted human CSF and incubated them with THP-1 macrophages. Immunofluorescence staining and time-lapse recording techniques were performed to evaluate the phagocytosis. We also immunostained human hippocampal sections to study possible interactions between wasteosomes and macrophages at central nervous system interfaces.
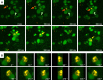
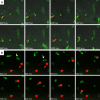
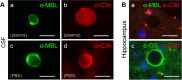
Results: We observed that the wasteosomes obtained from post-mortem extracted CSF are opsonized by MBL and the C3b complement protein. Moreover, we observed that CD206 and CD35 receptors may be involved in the phagocytosis of these wasteosomes by THP-1 macrophages. Once phagocytosed, wasteosomes become degraded and some of the resulting fractions can be exposed on the surface of macrophages and interchanged between different macrophages. However, brain tissue studies show that, in physiological conditions, CD206 but not CD35 receptors may be involved in the phagocytosis of wasteosomes.
Conclusions: The present study indicates that macrophages have the machinery required to process and degrade wasteosomes, and that macrophages can interact in different ways with wasteosomes. In physiological conditions, the main mechanism involve CD206 receptors and M2 macrophages, which trigger the phagocytosis of wasteosomes without inducing inflammatory responses, thus avoiding tissue damage. However, altered wasteosomes like those obtained from post-mortem extracted CSF, which may exhibit waste elements, become opsonized by MBL and C3b, and so CD35 receptors constitute another possible mechanism of phagocytosis, leading in this case to inflammatory responses.
Keywords: Brain; C3b; CD206; CD35; Corpora amylacea; IgM; Natural immunity; Phagocytosis; Wasteosome.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Wasteosomes (corpora amylacea) as a hallmark of chronic glymphatic insufficiency.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Nov 29;119(48):e2211326119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2211326119. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36409907 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering tau in wasteosomes (corpora amylacea) of Alzheimer's disease patients.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Mar 30;15:1110425. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1110425. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37065464 Free PMC article.
-
From corpora amylacea to wasteosomes: History and perspectives.Ageing Res Rev. 2021 Dec;72:101484. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2021.101484. Epub 2021 Oct 9. Ageing Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 34634491 Review.
-
Corpora amylacea act as containers that remove waste products from the brain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Dec 17;116(51):26038-26048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1913741116. Epub 2019 Dec 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31796594 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing the Virchow pioneering report on brain corpora amylacea: shedding light on recurrent controversies.Brain Struct Funct. 2023 Jul;228(6):1371-1378. doi: 10.1007/s00429-023-02664-5. Epub 2023 Jun 26. Brain Struct Funct. 2023. PMID: 37358661 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endothelial cells and macrophages as allies in the healthy and diseased brain.Acta Neuropathol. 2024 Feb 12;147(1):38. doi: 10.1007/s00401-024-02695-0. Acta Neuropathol. 2024. PMID: 38347307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corpora amylacea negatively correlate with hippocampal tau pathology in Alzheimer's disease.Front Neurosci. 2024 Feb 29;18:1286924. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1286924. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38486969 Free PMC article.
-
Wasteosomes (corpora amylacea) as a hallmark of chronic glymphatic insufficiency.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Nov 29;119(48):e2211326119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2211326119. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36409907 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering tau in wasteosomes (corpora amylacea) of Alzheimer's disease patients.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Mar 30;15:1110425. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1110425. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37065464 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid-Forming Corpora Amylacea and Spheroid-Type Amyloid Deposition: Comprehensive Analysis Using Immunohistochemistry, Proteomics, and a Literature Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 4;25(7):4040. doi: 10.3390/ijms25074040. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612850 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

