Microglia in motor neuron disease: Signaling evidence from last 10 years
- PMID: 36309345
- PMCID: PMC9828749
- DOI: 10.1002/dneu.22905
Microglia in motor neuron disease: Signaling evidence from last 10 years
Abstract
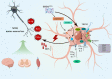
Motor neuron disease (MND), including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, spinal muscular atrophy and others, involved the upper or lower motor neurons selective loss, is characterized by neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation, in conjunction with microglia. We summarized that pathways and key mediators are associated with microglia, such as fractalkine signaling, purinergic signaling, NF-κB signaling, p38 MAPK signaling, TREM2-APOE signaling, ROCK signaling, C1q signaling, and Ion channel, which are involved in the activation, proliferation, and inflammation of microglia. This review aims to identify the microglia-related molecular target and explore potential treatment strategies for MND based on that target.
Keywords: ALS; MND; microglia; neuroinflammation; signaling.
© 2022 The Authors. Developmental Neurobiology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ando, S. , Osanai, D. , Takahashi, K. , Nakamura, S. , Shimazawa, M. , & Hara, H. (2020). Survival motor neuron protein regulates oxidative stress and inflammatory response in microglia of the spinal cord in spinal muscular atrophy. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences, 144(4), 204–211. 10.1016/j.jphs.2020.09.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous