Learning multi-agent cooperation
- PMID: 36310631
- PMCID: PMC9616006
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbot.2022.932671
Learning multi-agent cooperation
Abstract
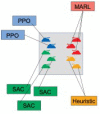
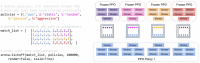
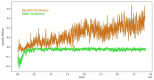
Advances in reinforcement learning (RL) have resulted in recent breakthroughs in the application of artificial intelligence (AI) across many different domains. An emerging landscape of development environments is making powerful RL techniques more accessible for a growing community of researchers. However, most existing frameworks do not directly address the problem of learning in complex operating environments, such as dense urban settings or defense-related scenarios, that incorporate distributed, heterogeneous teams of agents. To help enable AI research for this important class of applications, we introduce the AI Arena: a scalable framework with flexible abstractions for associating agents with policies and policies with learning algorithms. Our results highlight the strengths of our approach, illustrate the importance of curriculum design, and measure the impact of multi-agent learning paradigms on the emergence of cooperation.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; learned cooperation; multi-agent; policy learning; reinforcement learning.
Copyright © 2022 Rivera, Staley and Llorens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



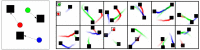
References
-
- Abel D. (2019). Simple_rl: reproducible reinforcement learning in python, in RML@ ICLR (New Orleans, LA: ).
-
- Bengio Y., Louradour J., Collobert R., Weston J. (2009). Curriculum learning, in Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning (New York, NY: ), 41–48. 10.1145/1553374.1553380 - DOI
-
- Cai Y., Yang S. X., Xu X. (2013). A combined hierarchical reinforcement learning based approach for multi-robot cooperative target searching in complex unknown environments, in 2013 IEEE Symposium on Adaptive Dynamic Programming and Reinforcement Learning (ADPRL) (Singapore: ), 52–59. 10.1109/ADPRL.2013.6614989 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

