DNase inhibits early biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa- or Staphylococcus aureus-induced empyema models
- PMID: 36310876
- PMCID: PMC9597695
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.917038
DNase inhibits early biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa- or Staphylococcus aureus-induced empyema models
Abstract
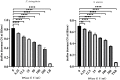
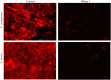
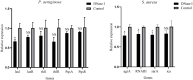
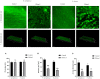
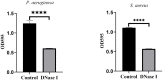
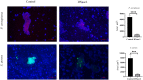
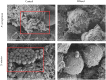
Anti-infection strategies against pleural empyema include the use of antibiotics and drainage treatments, but bacterial eradication rates remain low. A major challenge is the formation of biofilms in the pleural cavity. DNase has antibiofilm efficacy in vitro, and intrapleural therapy with DNase is recommended to treat pleural empyema, but the relevant mechanisms remain limited. Our aim was to investigate whether DNase I inhibit the early biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa- or Staphylococcus aureus-induced empyema models. We used various assays, such as crystal violet staining, confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) analysis, peptide nucleic acid-fluorescence in situ hybridization (PNA-FISH), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis. Our results suggested that DNase I significantly inhibited early biofilm formation in a dose-dependent manner, without affecting the growth of P. aeruginosa or S. aureus in vitro. CLSM analysis confirmed that DNase I decreased the biomass and thickness of both bacterial biofilms. The PNA-FISH and SEM analyses also revealed that DNase I inhibited early (24h) biofilm formation in two empyema models. Thus, the results indicated that DNase inhibited early (24h) biofilm formation in P. aeruginosa- or S. aureus-induced rabbit empyema models and showed its therapeutic potential against empyema biofilms.
Keywords: DNase; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Staphylococcus aureus; biofilm; pleural empyema.
Copyright © 2022 Deng, Lei, Tang, Li, Liang, Luo, Liu, Zhang, Ye, Kong, Wang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Banu S. F., Rubini D., Rakshitaa S., Chandrasekar K., Murugan R., Wilson A., et al. . (2017). Antivirulent properties of underexplored cinnamomum tamala essential oil and its synergistic effects with DNase against pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms – an In vitro study. Front. Microbiol. 8. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01144 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

