Advances in orthodontic clear aligner materials
- PMID: 36311049
- PMCID: PMC9588987
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.10.006
Advances in orthodontic clear aligner materials
Abstract
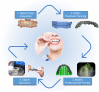
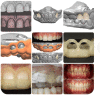
Rapid technological improvements in biomaterials, computer-aided design (CAD) and manufacturing (CAM) have endorsed clear aligner therapy (CAT) as a mainstay of orthodontic treatment, and the materials employed for aligner fabrication play an all-important role in determining the clinical performance of clear aligners. This narrative review has attempted to comprehensively encompass the entire gamut of materials currently used for the fabrication of clear aligners and elucidate their characteristics that are crucial in determining their performance in an oral environment. Historical developments and current protocols in aligner fabrication, features of contemporary bioactive materials, and emerging trends related to CAT are discussed. Advances in aligner material chemistry and engineering possess the potential to bring about radical transformations in the therapeutic applications of CAT; in the absence of which, clear aligners would continue to underperform clinically, due to their inherent biomechanical constraints. Finally, while innovations in aligner materials such as shape memory polymers, direct three-dimensional (3D) printed clear aligners and bioactive materials combined with clear aligner materials are essential to further advance the applications of CAT; increased awareness of environmental responsibilities among aligner manufacturers, aligner prescribing clinicians and aligner users is essential for better alignment of our climate change goals towards a sustainable planet.
Keywords: Bioactive materials; Clear aligners; Direct 3D printing; Environment; Review; Shape memory polymers.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures





References
-
- Lee R. Invisible orthodontics market: North American market remains solid, Chinese market grows rapidly. 3D Printing—Int. Mag. Dent. Print. Technol. 2022;2(1):46–47.
-
- Hartshorne J., Wertheimer M.B. Emerging insights and new developments in clear aligner therapy: a review of the literature. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. Clin. Companion. 2022;2(4):311–324.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

